Types of Conveyor Pulleys: A Complete Guide
Conveyor systems are the backbone of material handling across industries such as mining, manufacturing, warehousing, logistics, and food processing. At the heart of every conveyor system lies the conveyor pulley, a key component that drives, supports, and redirects the conveyor belt. Without the right pulley, a conveyor system cannot function efficiently, making it essential for businesses to understand the different types available and their specific roles.
In this complete guide, we will explore the types of conveyor pulleys that play a vital role in ensuring smooth operations. From drive pulleys (head pulleys) that provide the power, to idler pulleys that guide the belt, and snub or take-up pulleys that maintain tension, each type is designed to perform a unique function. Modern variations such as motorized pulleys, v-belt pulleys, and timing belt pulleys further enhance performance, energy efficiency, and durability.
By understanding these pulley types, businesses can select the right equipment for their operations, reduce downtime, and extend the lifespan of their conveyor systems. This guide is designed to give you a clear, practical understanding of conveyor pulleys, helping you make informed decisions for improved productivity and cost savings. For complete solutions, working with a trusted conveyor gearbox manufacturer ensures efficiency and long-term reliability.
What Is Conveyor Pulley
Conveyor pulleys are essential components that keep belt conveyor systems working efficiently. They guide, drive, and support the belt while handling tension and load. Different industries use specific pulleys depending on the type of material being transported, the operating environment, and system design. Knowing the main types of conveyor pulleys helps in choosing the right equipment for long-lasting performance and smooth operation.
Here are the most common types:
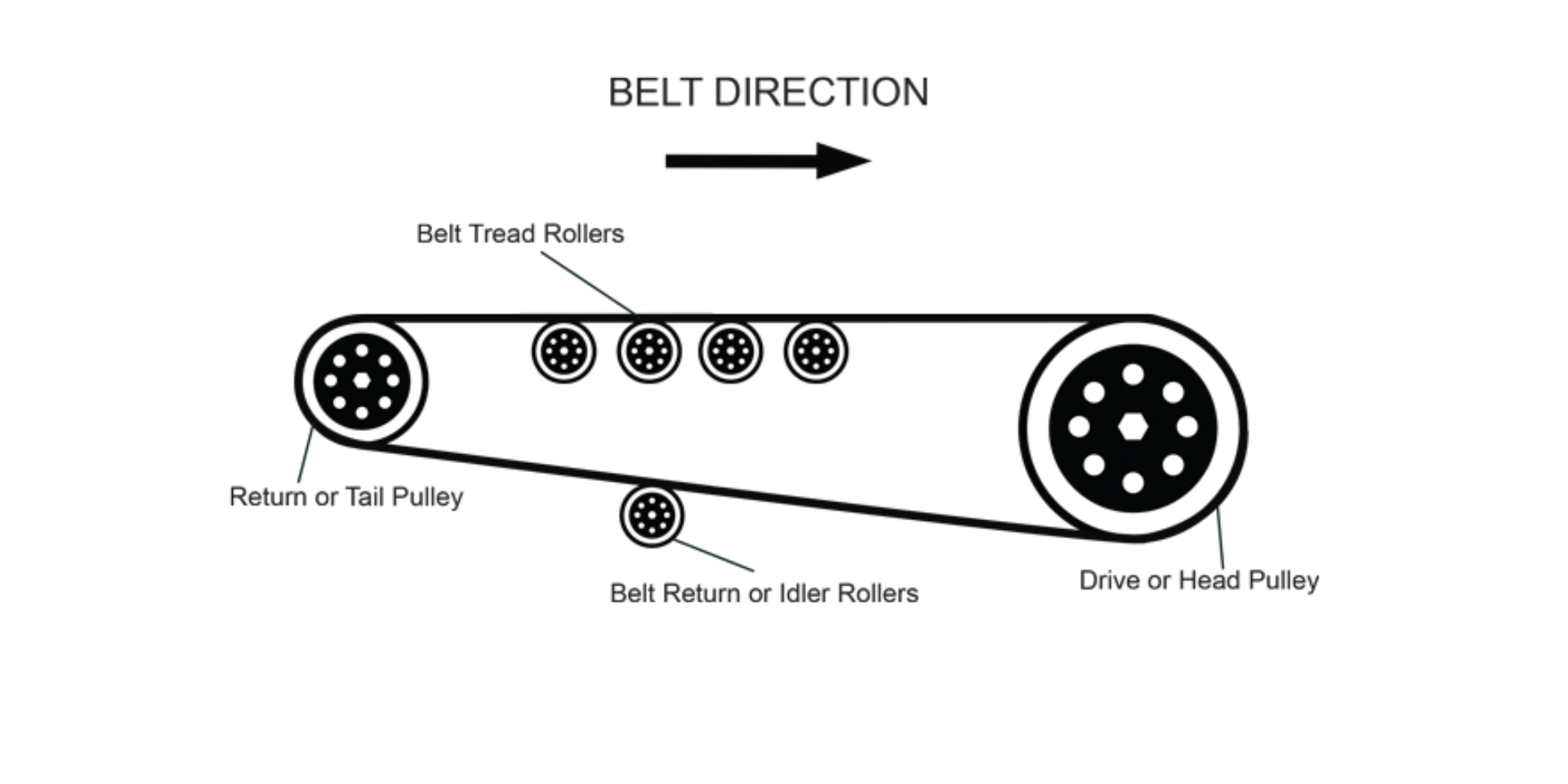
1. Drive Pulley
The Drive Pulley, also known as the Head Pulley, is the heart of any conveyor system. It is the primary component that provides the driving force to move the conveyor belt and the materials placed on it.
Positioned at the discharge end of the conveyor, the drive pulley is connected to the motor and transmits torque through the belt. Without this critical element, the conveyor system would not function efficiently, as it is responsible for converting motor energy into continuous belt movement.
Role of the Drive Pulley in Conveyor Systems
The drive pulley (head pulley) performs several crucial functions that ensure the reliability of the entire system:
- Power Transmission: Transfers power from the motor to the belt, enabling movement.
- Material Flow: Controls the speed at which materials travel on the conveyor.
- Belt Alignment: Keeps the conveyor belt properly aligned, reducing chances of belt drift.
- Friction & Grip: When lagged with rubber or ceramic, it improves friction to prevent slippage.
- System Stability: Ensures consistent performance, even under heavy loads.
Advantages of Using a Drive Pulley
Industries prefer using a well-designed drive pulley because it:
- Prevents belt slippage, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
- Extends the lifespan of conveyor belts by reducing wear.
- Improves energy efficiency by minimizing power loss.
- Handles high-load conditions without system breakdown.
- Provides smooth and consistent material handling.
Applications of Drive Pulley
The drive pulley is widely used across industries that rely on conveyor systems, such as:
- Mining & Quarrying: For transporting ores, coal, and minerals.
- Cement & Construction: To move raw materials and cement clinker.
- Food Processing & Packaging: Hygienic conveyors for bulk goods.
- Logistics & Warehousing: Ensures efficient handling of packages.
- Manufacturing Units: Keeps assembly lines moving with steady product flow.
2. Tail Pulley
The Tail Pulley is an essential part of any conveyor system. Located at the opposite end of the conveyor from the drive pulley, it plays a crucial role in returning the belt back to the drive system while maintaining proper alignment.
Although it does not supply power like the head pulley, the tail pulley ensures smooth belt movement, reduces tension issues, and helps prevent misalignment. Its position and design directly affect the efficiency and lifespan of the conveyor belt.
Role of the Tail Pulley in Conveyor Systems
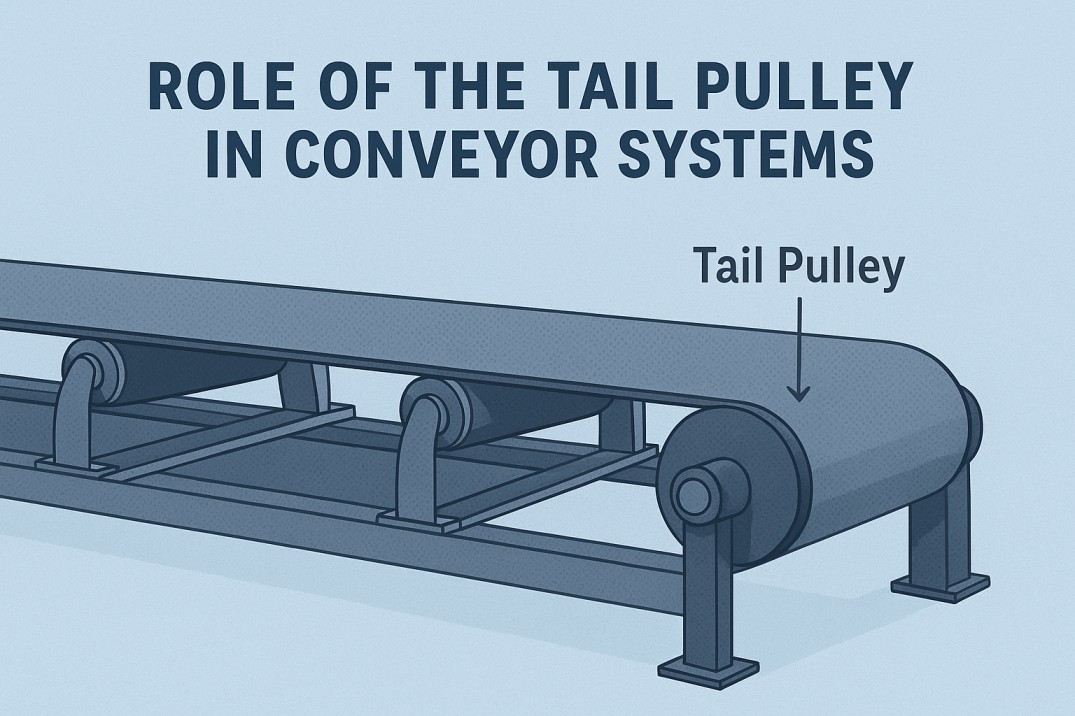
The tail pulley is more than just a support component. It is designed to guide and stabilize the conveyor belt as it completes its return cycle. Some of its main roles include:
- Belt Return: Redirects the conveyor belt back to the drive pulley.
- Alignment Support: Keeps the belt centered and aligned, reducing tracking problems.
- Tension Adjustment: Works with other pulleys to help maintain balanced belt tension.
- Load Carrying: Provides stable support for the return side of the belt.
- System Balance: Reduces wear on the belt by minimizing unnecessary strain.
Types of Tail Pulley
Depending on the system’s requirement, tail pulleys can be designed in different forms:
- Flat Tail Pulley: Standard design used in light-duty conveyors.
- Wing Tail Pulley: Built with open wings to prevent material buildup, especially in mining and bulk handling industries.
- Crowned Tail Pulley: Slightly curved surface to improve belt tracking and reduce misalignment.
Advantages of Using a Tail Pulley
Installing the right type of tail pulley offers several advantages:
- Extends the life of the conveyor belt by preventing uneven wear.
- Maintains smooth belt movement, reducing downtime.
- Improves safety by avoiding belt slippage and misalignment.
- Handles bulk materials effectively in both light and heavy-duty operations.
- Reduces maintenance costs by minimizing material buildup and belt stress.
Applications of Tail Pulley
The tail pulley is widely used in industries where continuous material handling is critical. Some applications include:
- Mining & Quarrying: Manages the return belt under heavy loads.
- Construction & Cement Plants: Ensures reliable handling of raw materials.
- Agriculture & Food Processing: Keeps belts aligned in bulk grain and product movement.
- Logistics & Warehousing: Provides stability for package handling conveyors.
- Manufacturing Units: Maintains efficient return of belts in assembly line operations.
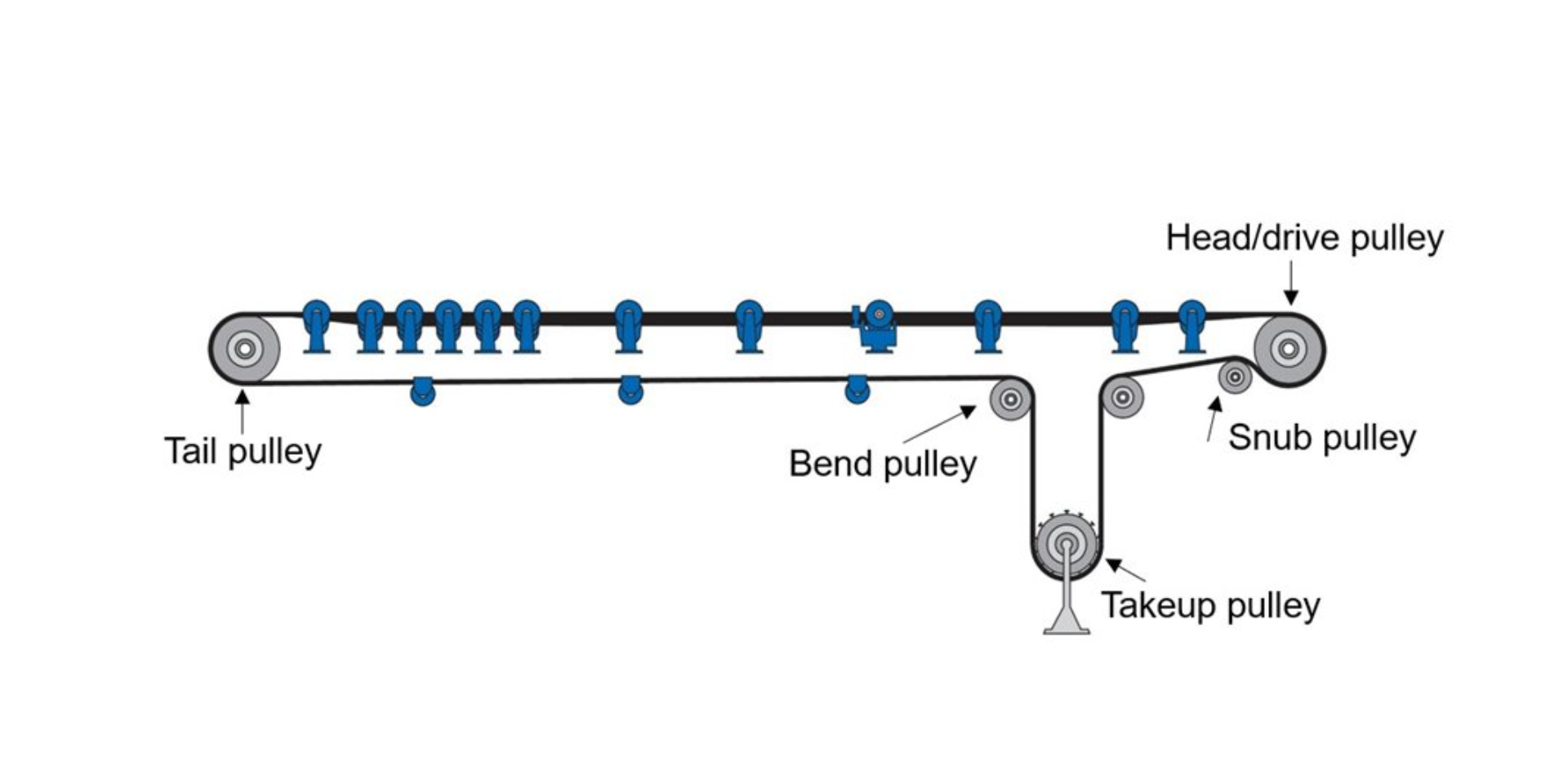
3. Snub Pulley
Without proper belt tension, a conveyor system may experience slippage, misalignment, or premature wear. By automatically adjusting to changes in belt length caused by temperature, load, or stretching, the take-up pulley keeps operations running smoothly and safely. Understanding what is pulley in conveyor systems helps businesses realize the importance of take-up pulleys in maintaining efficiency and reducing downtime.
Role of the Take-Up Pulley in Conveyor Systems
The take-up pulley plays a crucial role in both light-duty and heavy-duty conveyor systems. Its main roles include:
- Tension Control: Maintains proper belt tightness to avoid slippage.
- Alignment Support: Keeps the conveyor belt running straight and stable.
- Shock Absorption: Adapts to belt elongation caused by heavy loads.
- Wear Reduction: Reduces stress on the belt and prevents uneven stretching.
- Smooth Operations: Ensures efficient power transfer from the drive pulley.
Types of Take-Up Pulley
Different conveyor systems use different types of take-up pulley mechanisms:
- Fixed Take-Up Pulley: Set in one position and manually adjusted when needed.
- Automatic Take-Up Pulley: Self-adjusting design that continuously regulates belt tension.
- Gravity Take-Up Pulley: Uses counterweights to maintain tension automatically.
- Horizontal Take-Up Pulley: Installed in horizontal arrangements for specific conveyor setups.
Applications of Take-Up Pulley
The take-up pulley is widely used in industries that rely on continuous material handling. Some of the key applications include:
- Mining and Quarrying: Ensures reliable belt performance under heavy loads.
- Cement Plants: Maintains smooth handling of raw materials.
- Steel & Power Industries: Provides stability in bulk transportation of ores and fuels.
- Logistics & Warehousing: Prevents belt slack in high-volume package conveyors.
- Agriculture & Food Industry: Keeps belts properly tensioned during grain and food transport.
4. Idler Pulley
The Idler Pulley is a key component in conveyor systems that helps support and guide the belt along its path. Unlike the drive pulley or tail pulley, the idler pulley does not supply power. Instead, it works as a stabilizer, ensuring that the belt remains aligned, free from sagging, and able to handle the load efficiently. This makes it one of the most widely used pulleys in both light-duty and heavy-duty conveyor applications.
By reducing stress on the belt and maintaining smooth movement, the idler pulley improves the overall efficiency and reliability of conveyor systems. It is a cost-effective yet critical part of bulk material handling, packaging, and industrial operations.
Role of the Idler Pulley in Conveyor Systems
The idler pulley plays a supportive but vital role in the working of conveyor belts. Some of its major functions include:
- Belt Support: Prevents sagging and keeps the belt stable during operation.
- Alignment Assistance: Guides the belt in a straight path, reducing tracking problems.
- Load Distribution: Shares weight evenly across the belt to reduce wear.
- Energy Efficiency: Minimizes resistance and friction, saving power.
- System Safety: Ensures smooth belt movement, reducing the risk of accidents.
Types of Idler Pulley
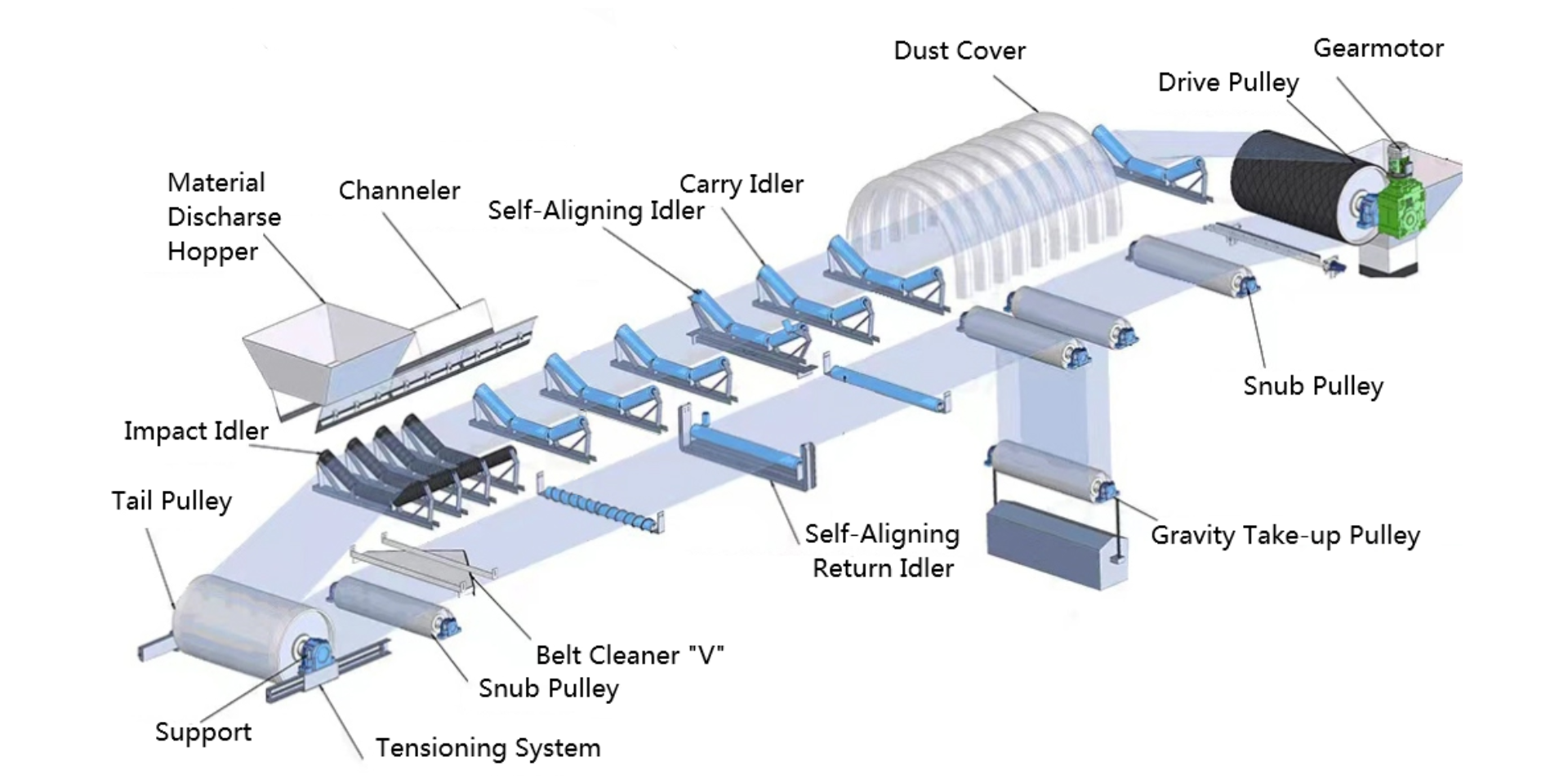
Depending on design and usage, the idler pulley comes in several types:
- Carrying Idler Pulley: Positioned on the loaded side of the conveyor to support materials.
- Return Idler Pulley: Found on the empty side, guiding the belt back to the head pulley.
- Impact Idler Pulley: Placed at loading points to absorb shock and reduce damage.
- Training Idler Pulley: Designed to correct belt misalignment and tracking errors.
Applications of Idler Pulley
The idler pulley is versatile and used in a wide range of industries, including:
- Mining & Quarrying: For transporting bulk ores, coal, and minerals.
- Cement Plants: To ensure smooth handling of heavy raw materials.
- Agriculture & Food Processing: For grain, seeds, and packaged goods.
- Logistics & Warehousing: To support belts moving parcels and boxes.
- Manufacturing Units: For stable operations in assembly line conveyors.
5. Motorized Pulley
The Motorized Pulley is a modern and highly efficient drive solution for conveyor systems. Unlike traditional pulleys that require external motors, gearboxes, and chain drives, a motorized pulley houses the motor, gearbox, and bearings inside a sealed drum shell. This compact design provides continuous power while saving space, reducing maintenance, and improving safety.
The motorized pulley is especially popular in industries where hygiene, efficiency, and compact installation are essential. From airports and food processing to mining and logistics, this advanced pulley design is becoming the preferred choice for conveyor operations worldwide.
Role of the Motorized Pulley in Conveyor Systems
The motorized pulley performs several key functions that make it superior to conventional drive setups:
- Integrated Drive System: Combines motor, gearbox, and bearings in one sealed unit.
- Space Saving: Eliminates bulky external drive components.
- Continuous Power Transmission: Provides smooth and reliable belt movement.
- Low Maintenance: Protected design reduces dust and water ingress.
Enhanced Safety: Fewer exposed parts mean reduced accident risks.
Types of Motorized Pulley
Depending on the application, motorized pulleys are available in different configurations:
- Standard Motorized Pulley: Used in general material handling and logistics.
- Heavy-Duty Motorized Pulley: Built for mining, cement, and steel plants with demanding loads.
- Food-Grade Motorized Pulley: Designed with stainless steel and hygienic seals for food and pharmaceutical industries.
Explosion-Proof Motorized Pulley: Used in industries where safety against fire or explosion is critical.
Applications of Motorized Pulley
The motorized pulley is versatile and widely used in industries across the globe:
- Airports & Logistics Hubs: Smooth baggage and parcel handling.
- Food & Beverage Industry: Hygienic conveyors for food packaging and processing.
- Mining & Quarrying: Heavy-duty systems for transporting coal, minerals, and ores.
- Cement & Steel Plants: For bulk material handling in tough environments.
- E-commerce & Warehousing: Ensures efficient high-speed sorting and packaging.
6. V-Belt Drive Pulley
The V-Belt Drive Pulley is one of the most widely used mechanical components for transmitting power between shafts in industrial and automotive systems. It works in combination with a V-belt, which fits snugly into the grooves of the pulley. This design ensures maximum friction, efficient torque transfer, and reduced chances of slippage. The V-belt drive pulley is popular because it offers quiet operation, flexibility in speed adjustment, and the ability to handle high power loads with minimal maintenance.
Unlike flat pulleys, the V-belt drive pulley uses a wedge-shaped design that allows the belt to grip tightly as load increases. This self-tightening feature makes it highly efficient for both light-duty and heavy-duty applications.
Role of the V-Belt Drive Pulley in Conveyor Systems
The V-belt drive pulley performs several important functions in industrial and mechanical systems:
- Torque Transfer: Transmits power from the motor to driven equipment.
- Slip Reduction: Provides higher friction compared to flat pulleys.
- Load Handling: Capable of handling heavy loads smoothly.
- Speed Adjustment: Enables flexibility by changing pulley sizes.
- Durability: Works reliably under continuous operation.
Types of V-Belt Drive Pulley
The V-belt drive pulley comes in different designs depending on the belt arrangement:
- Single Groove Pulley: Used for low-power transmission with one V-belt.
- Multiple Groove Pulley: Handles high-power loads with several belts running parallel.
- Variable Pitch Pulley: Allows adjustable speed by changing the belt’s running diameter.
- Flat with V-Groove Combination: Used in specialized machinery for combined applications.
Applications of V-Belt Drive Pulley
The V-belt drive pulley is versatile and used in multiple industries, such as:
- Automobiles: Powers alternators, compressors, and pumps.
- Agriculture: Drives equipment like threshers, harvesters, and conveyors.
- Manufacturing Plants: Runs machines such as lathes, mills, and compressors.
- HVAC Systems: Powers fans, blowers, and cooling systems.
- Mining & Quarrying: Used in conveyors and crushers for heavy-duty operations.
7. Timing Belt Pulley
The Timing Belt Pulley is a highly specialized component designed for precision-driven applications. Unlike flat or V-belt pulleys, the timing belt pulley features grooves that match with the teeth of a timing belt. This unique tooth-and-groove engagement ensures positive drive transmission, meaning there is no slippage between the belt and pulley. As a result, the system delivers accurate speed, synchronized motion, and efficient power transfer.
The timing belt pulley is widely used in industries and machines where accuracy is critical, such as robotics, automobiles, printing, and packaging equipment. Its ability to provide reliable synchronization makes it a p
Role of the Timing Belt Pulley in Conveyor Systems
The timing belt pulley performs essential roles that make it stand out in power transmission:
- Positive Drive Transmission: Prevents belt slippage with tooth engagement.
- Synchronization: Ensures precise timing between shafts and equipment.
- Efficiency: Delivers smooth power with minimal energy loss.
- Durability: Reduces wear by maintaining constant contact.
- Noise Reduction: Operates more quietly than chain or gear drives.
Types of Timing Belt Pulley
- Standard Timing Pulley: Basic design for general machinery and automation.
- Flanged Timing Pulley: Includes flanges to prevent belt movement and misalignment.
- Double-Sided Timing Pulley: Works with double-sided timing belts for multi-directional drives.
- Custom Timing Pulley: Designed for unique industry-specific applications.
Applications of Timing Belt Pulley
The timing belt pulley has a wide range of applications where precision is critical:
- Automobiles: Powers camshafts and crankshafts to maintain engine timing.
- Robotics & Automation: Ensures synchronized motion in robotic arms and conveyors.
- Textile & Printing Industries: Provides accurate machine timing for seamless operations.
- Packaging Industry: Delivers smooth and precise product handling.
- Medical Equipment: Used in devices requiring accuracy and reliability.
8. Wing Pulley
The Wing Pulley is a specialized pulley designed to keep conveyor belts running smoothly while preventing material build-up. Unlike standard flat pulleys, the wing pulley features angled metal wings or bars across its surface. As the belt passes over, these wings deflect loose material, dirt, and debris away from the pulley. This self-cleaning design is especially useful in industries that handle bulk materials such as mining, quarrying, agriculture, and construction.
The wing pulley not only increases conveyor efficiency but also helps extend the life of the belt by reducing unnecessary wear and tear caused by trapped materials. It is mainly installed at the tail section of a conveyor system, where material carryback and spillage are more likely to occur. For industries focused on effective material separation and smooth conveyor performance, partnering with a trusted suspension magnet manufacturer ensures enhanced productivity and long-term reliability.
Role of the Wing Pulley in Conveyor Systems
The wing pulley performs several critical roles that improve conveyor performance:
- Self-Cleaning Action: Deflects dirt, debris, and wet material away from the pulley.
- Prevents Build-Up: Reduces clogging, which can cause belt misalignment.
- Protects Belt Surface: Prevents sharp material from damaging the belt.
- Increases Belt Life: Reduces wear caused by trapped materials.
- Supports Return Belt: Guides and stabilizes the belt in its return path.
Types of Wing Pulley
Depending on material type and operating conditions, wing pulleys are available in different forms:
- Standard Wing Pulley: Traditional open-wing design for light to medium applications.
- Heavy-Duty Wing Pulley: Built with stronger steel bars for mining and quarry conveyors.
- Spiral Wing Pulley: Angled wings in a spiral design for smoother operation and reduced vibration.
- Ceramic-Coated Wing Pulley: Offers extra grip and durability in abrasive environments.
Applications of Wing Pulley
The wing pulley is widely used in bulk material handling industries where contamination and build-up are common. Key applications include:
- Mining & Quarrying: For coal, stone, and mineral conveyors.
- Cement & Construction: Reduces debris build-up in heavy-duty conveyors.
- Agriculture: Prevents clogging in grain and feed handling systems.
- Recycling Plants: Handles bulk waste and scrap materials.
- Power Plants: Ensures smooth transport of ash and raw fuel materials.
9. Bend Pulley
The Bend Pulley is an important component of conveyor systems, mainly used to change the direction of the belt and improve its contact with other pulleys. Unlike the drive pulley, which transmits power, the bend pulley functions as a support and redirection unit. By guiding the belt at different angles, it helps the conveyor achieve the required path, improves tension, and enhances overall efficiency.
In most systems, the bend pulley is installed close to the drive or take-up pulley to increase the wrap angle. This ensures better grip, prevents belt slippage, and allows the conveyor to handle heavy loads with consistency. Though simple in design, the bend pulley plays a critical role in maintaining smooth and stable operations. For industries seeking reliable material handling solutions, choosing components from a trusted SMSR Gearbox manufacturer ensures durability, efficiency, and long-term performance.
Role of the Bend Pulley in Conveyor Systems
The bend pulley ensures efficient belt movement and alignment by performing several roles:
- Belt Redirection: Changes the direction of the conveyor belt smoothly.
- Increases Wrap Angle: Provides additional contact with the drive pulley for better grip.
- Tension Distribution: Helps maintain proper belt tension across the system.
- Alignment Support: Keeps the belt tracking correctly to avoid misalignment.
- Load Handling: Improves belt performance under heavy loads.
Types of Bend Pulley
Depending on the system requirements, the bend pulley comes in different designs:
- Flat Bend Pulley: Standard type for light- to medium-duty conveyors.
- Lagged Bend Pulley: Rubber-coated for better grip and reduced slippage.
- Heavy-Duty Bend Pulley: Built for mining, quarrying, and bulk material handling.
- Crowned Bend Pulley: Slightly curved surface for improved belt tracking.
Applications of Bend Pulley
The bend pulley is commonly used in industries that rely on long and heavy-duty conveyor systems. Some applications include:
- Mining & Quarrying: Provides better belt grip for transporting coal, minerals, and ores.
- Cement Plants: Ensures stable belt alignment under heavy loads.
- Steel & Power Plants: Supports bulk handling of raw materials.
- Agriculture: Used in grain and bulk food handling conveyors.
- Logistics & Warehousing: Helps redirect belts in package handling systems.
Conclusion
The efficiency of any conveyor system largely depends on the pulleys that drive, guide, and support it. As we have seen, the different types of conveyor pulleys—including drive pulleys, tail pulleys, snub pulleys, idler pulleys, take-up pulleys, and motorized pulleys—each serve a specific function that contributes to smooth and reliable operations. From providing the driving force to maintaining belt alignment and reducing slippage, every pulley plays a vital role in extending the lifespan of conveyor belts and ensuring consistent productivity.
For industries such as mining, logistics, warehousing, food processing, and manufacturing, selecting the right pulley type is more than a technical decision—it’s an investment in safety, efficiency, and long-term cost savings. With advancements in technology, modern pulleys like motorized and timing belt pulleys offer even greater precision and energy efficiency, making them a preferred choice for many operations. Partnering with a reliable V-belt pulley manufacturer ensures durability, performance, and smooth operation across applications.
In conclusion, understanding the types of conveyor pulleys helps businesses make smarter choices that improve performance, reduce downtime, and support sustainable operations. Whether you are upgrading an existing system or designing a new one, the right pulley selection ensures your conveyor system remains reliable, cost-effective, and future-ready.
FAQS
What are the main types of conveyor pulleys?
The main types of conveyor pulleys include drive pulleys, tail pulleys, snub pulleys, take-up pulleys, idler pulleys, bend pulleys, wing pulleys, and motorized pulleys. Each serves a specific function, such as providing power, maintaining belt tension, redirecting the belt, or supporting smooth operation. Understanding these types helps industries choose the right pulley for efficient conveyor systems, reduced downtime, and long-term durability. Trusted manufacturers like Nisuka Industries offer high-quality pulley solutions designed to meet diverse industrial needs.
What is the role of a drive pulley in conveyor systems?
A drive pulley, also known as the head pulley, is responsible for supplying the driving force that moves the conveyor belt. It is typically motor-driven and located at the discharge end of the conveyor. This pulley is often covered with rubber or ceramic lagging to increase grip and reduce slippage. Among the different types of conveyor pulleys, the drive pulley is the most critical because it powers the entire system.
How does a tail pulley work in a conveyor system?
The tail pulley is positioned at the loading point of the conveyor. Its main role is to redirect the belt and provide a steady return path. In combination with other pulleys, it helps ensure the belt runs smoothly and efficiently. Many tail pulleys come with adjustable bearings to maintain alignment. Within the types of conveyor pulleys, the tail pulley is essential for preventing misalignment and ensuring proper material loading.
What is the purpose of a snub pulley?
A snub pulley increases the belt’s contact area with the drive pulley, enhancing traction and reducing slippage. By doing so, it ensures the conveyor system runs efficiently under heavy loads or high-speed conditions. Snub pulleys also assist in improving belt tracking and alignment. As one of the key types of conveyor pulleys, it is widely used in industries like mining and cement plants where strong grip and stability are essential.
Why are idler pulleys important in conveyor systems?
An idler pulley does not provide power but is crucial for supporting and guiding the belt. It reduces sagging, prevents misalignment, and extends the overall life of the belt. Idler pulleys are common in large conveyor systems used in mining, logistics, and packaging. As part of the types of conveyor pulleys, idlers ensure even load distribution, reduce friction, and keep operations consistent, making them indispensable in long-distance material handling.
What is the function of a take-up pulley?
The take-up pulley maintains proper belt tension by compensating for belt stretching or slack over time. It is especially important in long conveyor systems, where sagging can lead to misalignment and reduced efficiency. The take-up pulley ensures smooth operation and helps extend the life of the conveyor belt. In the list of types of conveyor pulleys, it is essential for keeping the system balanced and reducing maintenance costs.
How does a motorized pulley improve efficiency?
A motorized pulley, also called a drum motor, houses the motor inside the pulley shell. This compact design reduces the need for external drive components, making it safer, cleaner, and more efficient. Motorized pulleys require less maintenance, save space, and are energy efficient. Among modern types of conveyor pulleys, they are widely used in industries like food processing, airports, and packaging lines for continuous power and reliability.