What is a suspended magnet? Complete Guide
In today’s fast-growing industrial world, maintaining product purity and protecting machinery from metal contamination is more important than ever. One of the most effective tools used for this purpose is the Suspended Magnet. It plays a vital role in separating unwanted ferrous materials like iron, nails, and bolts from raw materials on conveyor belts.
A Suspended Magnet is a powerful magnetic separator installed above conveyor systems to attract and remove metal impurities from moving products. It ensures that only clean and safe materials continue through the production line, reducing downtime and equipment damage.
From industries such as mining, recycling, cement, coal, and food processing, suspended magnets have become essential for improving efficiency and product quality. Depending on the requirement, they can be permanent or electromagnetic, each designed for specific applications and performance levels.
In this complete guide, you’ll learn what a suspended magnet is, how it works, its types, advantages, and industrial uses — helping you understand why it’s one of the most reliable solutions in modern magnetic separation technology.
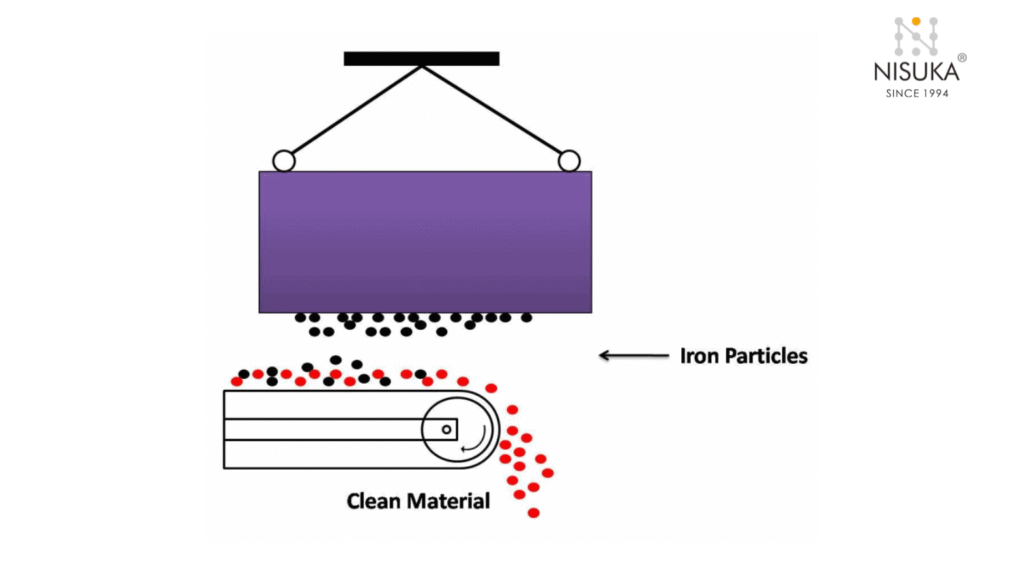
What Is a Suspended Magnet in Simple Terms?
In simple terms, What Is a Suspended Magnet refers to a strong magnetic device that hangs above a conveyor belt or material flow to catch and remove metal objects like nails, bolts, or scrap iron. It works by attracting ferrous materials using a magnetic field, ensuring that only clean, safe materials continue through the production line.
Industries such as mining, cement, recycling, and food processing use suspended magnets to protect machinery and maintain product quality. The magnet can be permanent or electromagnetic, depending on how powerful the separation process needs to be.
Choosing the right design and power depends on the type of material being processed and the level of contamination. For reliable quality and performance, it’s always recommended to work with an experienced Suspension magnet manufacturer who understands your industrial needs.
Simply put, What Is a Suspended Magnet — it’s a simple yet powerful solution that keeps your production clean, safe, and efficient.
Difference Between Suspended Magnet and Overband Magnet
Both suspended and overband magnets are used to remove metal contaminants, but they differ in cleaning method and functionality.
A suspended magnet is stationary and requires manual cleaning. It captures metallic impurities above the conveyor and holds them until someone cleans it off. This makes it suitable for low or medium contamination levels.
An overband magnet, however, comes with a self-cleaning belt system. The belt automatically moves the trapped metal away from the magnet, making it ideal for continuous or heavy-duty operations such as mining and recycling.
In short, What Is a Suspended Magnet is a cost-effective choice for moderate contamination, while an overband magnet offers automated cleaning and higher productivity. Both play a vital role in protecting equipment and improving process efficiency.
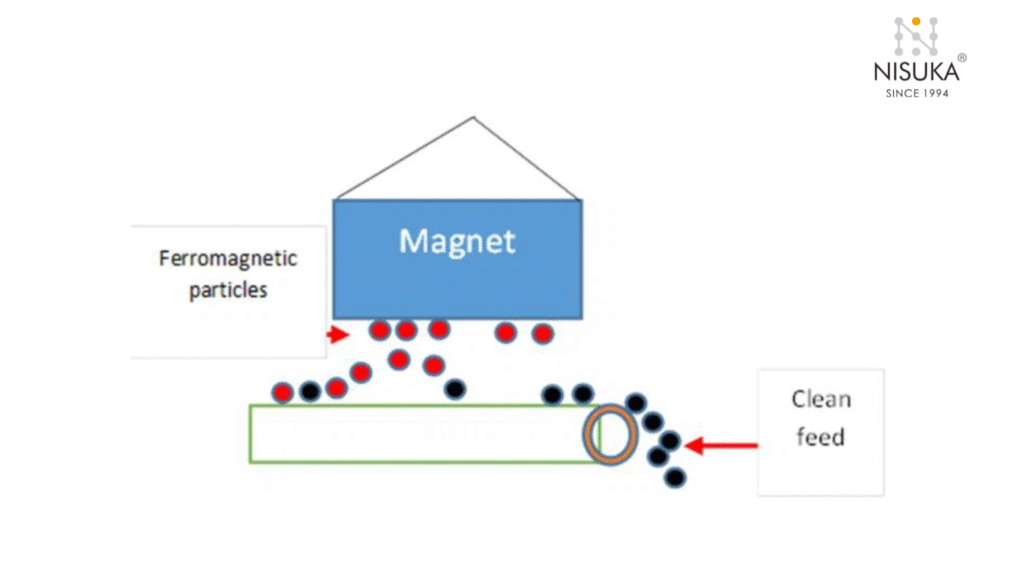
How Does a Suspended Magnet Work
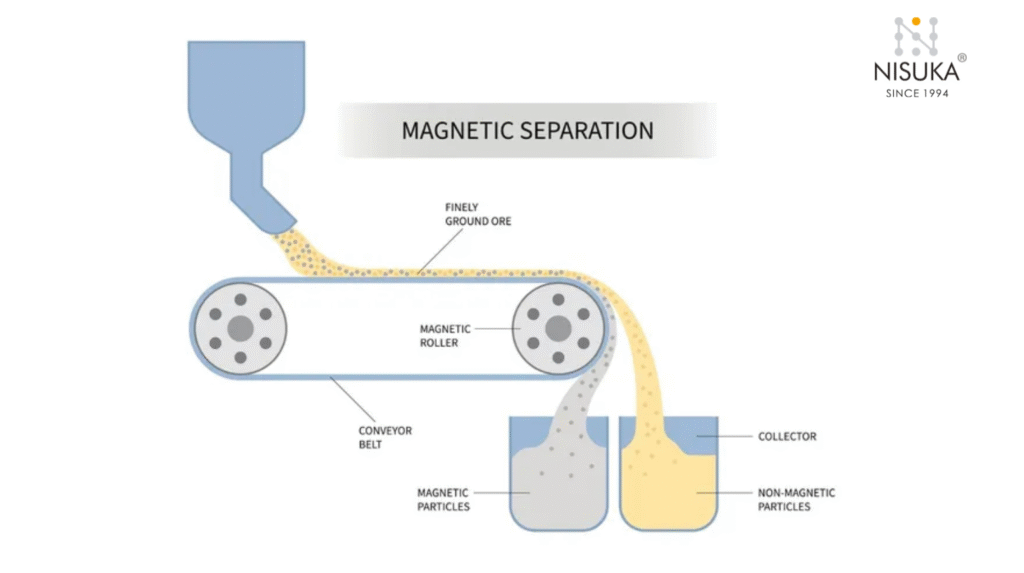
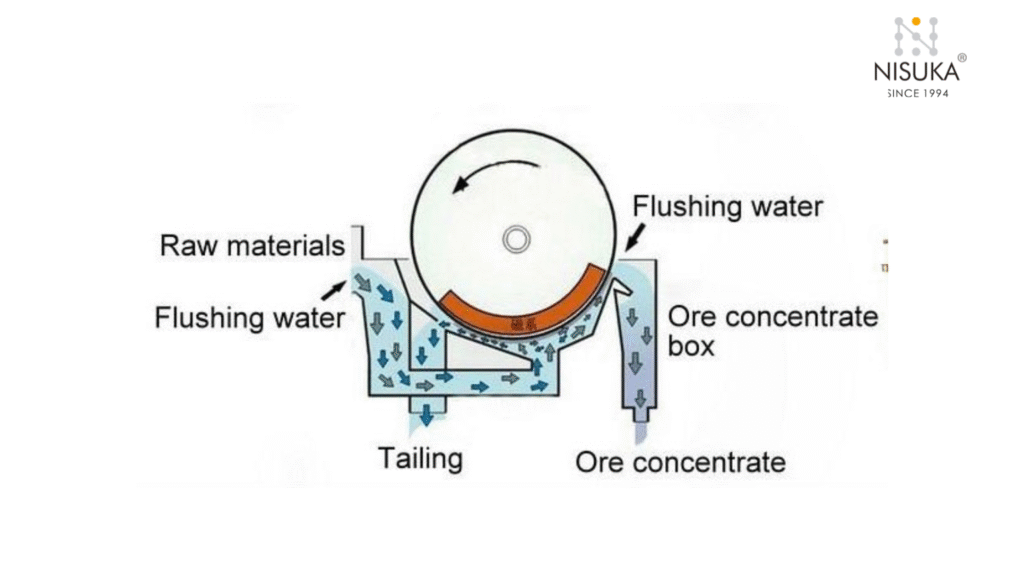
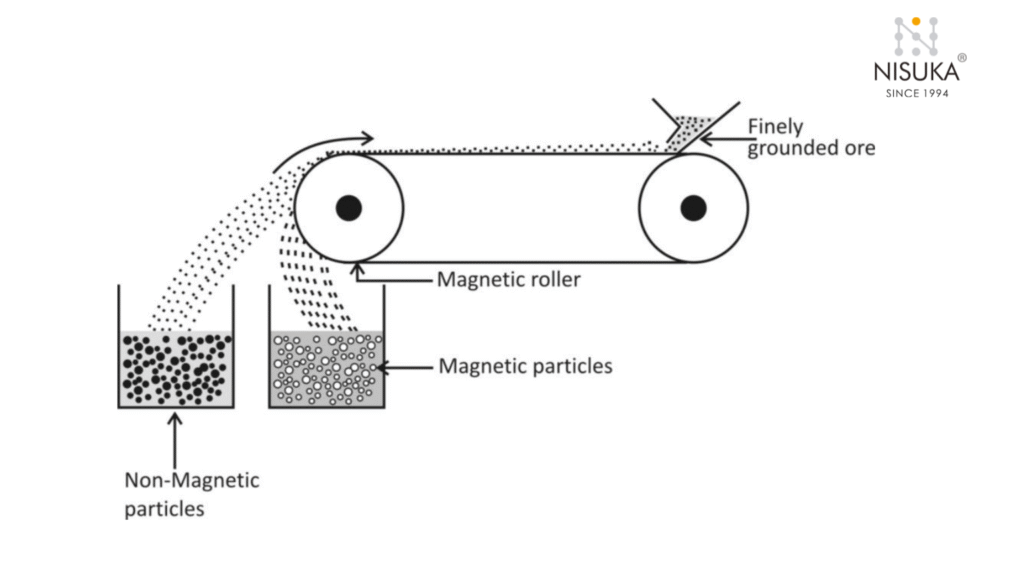
To understand How Does a Suspended Magnet Work, imagine a powerful magnet hanging above a moving conveyor belt filled with raw materials. As the material passes underneath, the suspended magnet creates a strong magnetic field that attracts and lifts any ferrous metals like nails, bolts, or iron fragments. These unwanted metals cling to the magnet, keeping them away from valuable material and protecting downstream machinery from damage.
How Does a Suspended Magnet Work depends on whether it’s a permanent magnet or an electromagnet. A permanent magnet uses natural magnetic force to attract metals, while an electromagnetic type generates a controlled magnetic field using electric current — allowing users to switch it on or off as needed.
Once the magnet captures metallic impurities, they can be removed manually or automatically, depending on the system design. This process ensures cleaner production, higher safety, and less machine downtime.
In industries such as mining, cement, and recycling, suspended magnets are vital for smooth operations and long-term efficiency. For companies focusing on mechanical reliability and machine alignment, consulting an expert Plummer block manufacturer can further enhance overall plant performance.
In short, How Does a Suspended Magnet Work — it continuously removes metal impurities through a powerful, automated separation process that ensures quality and protection in every production line.
Types of Suspended Magnets
Different Types of Suspended Magnets are designed to meet specific industrial requirements. They vary in power, cleaning style, and application areas, helping industries maintain clean material flow and protect machinery from metal contamination. Understanding these types helps in selecting the most effective magnetic separator for your system.
Permanent Suspended Magnets
Permanent suspended magnets are one of the most common Types of Suspended Magnets used in material handling. They generate a continuous magnetic field using high-intensity permanent magnets like ferrite or rare earth. Since they don’t require electricity, these magnets are cost-effective, energy-efficient, and ideal for continuous operations where metal contamination levels are moderate.
They are typically used in industries like cement, coal, and aggregate processing. Their low maintenance needs and consistent performance make them a preferred choice for operations that require reliable metal removal without extra power consumption.
Electromagnetic Suspended Magnets
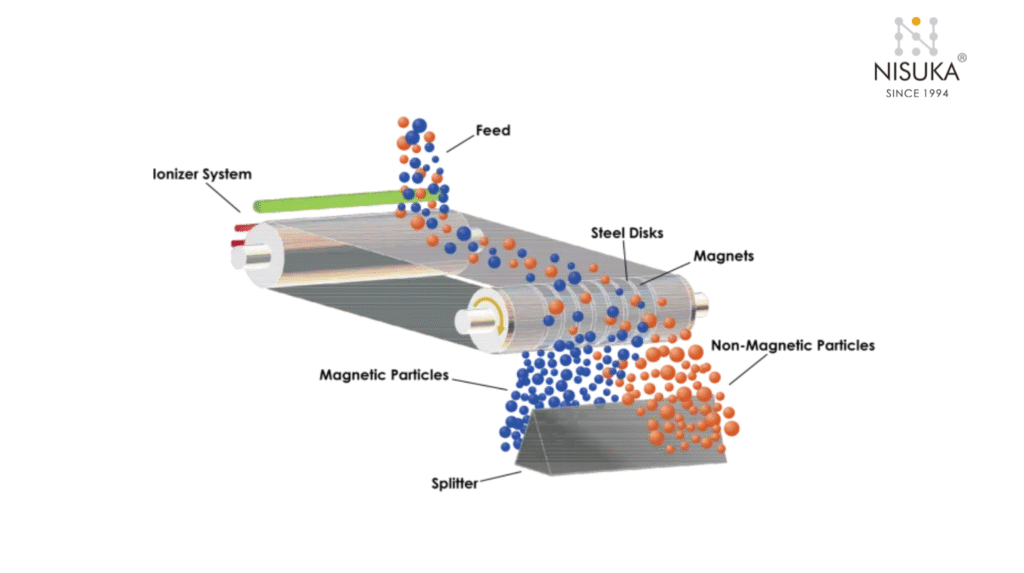
Electromagnetic suspended magnets are another major category under the Types of Suspended Magnets. These magnets use electric current to produce a powerful magnetic field, making them suitable for separating heavier or deeply buried ferrous contaminants.
A major advantage of these magnets is their adjustable magnetic strength, allowing operators to control the intensity as per material flow and contamination level. They are widely used in mining, recycling, and steel industries where high magnetic power is essential for efficiency.
When combined with proper machine support components from a reliable UCP Pillow block manufacturer, electromagnetic suspended magnets can operate smoothly and safely under demanding industrial conditions.
Manual vs. Self-Cleaning Suspended Magnets
Within different Types of Suspended Magnets, one important distinction is between manual cleaning and self-cleaning systems.
Manual suspended magnets require operators to stop the conveyor and physically remove trapped metal contaminants from the magnet surface. This type is suitable for smaller operations with minimal contamination.
Self-cleaning suspended magnets, on the other hand, come with a motorized conveyor belt system that continuously removes captured metals without interrupting the production line. These are preferred in industries that handle large volumes of material and demand continuous operation.
Choosing the Right Suspended Magnet for Your Industry
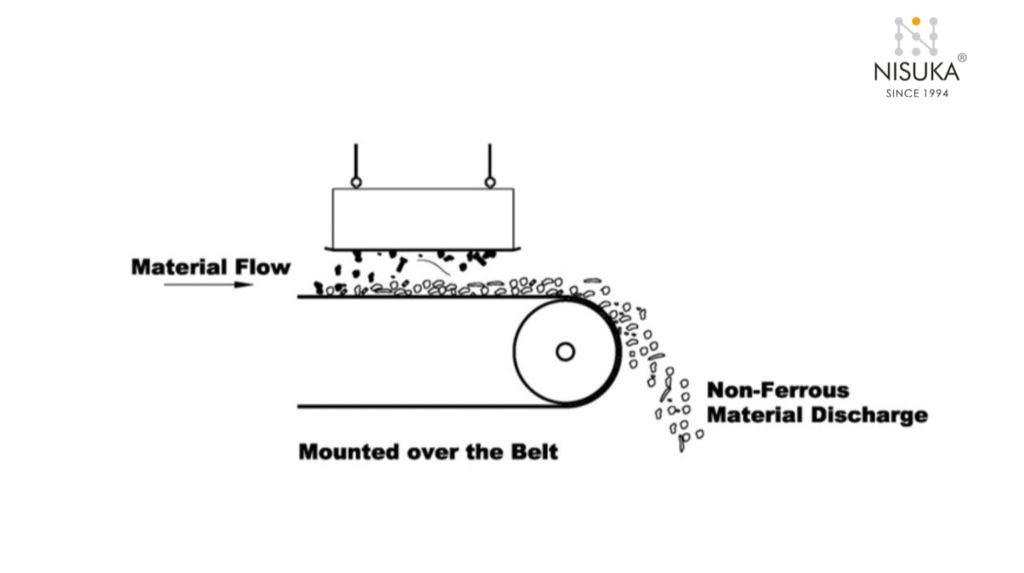
Choosing the right magnet from the available Types of Suspended Magnets depends on several factors — material type, contamination level, installation space, and operating environment.
For instance, if you handle lightweight materials with low contamination, a permanent magnet is usually enough. But for heavy-duty applications with dense or fast-moving materials, an electromagnetic suspended magnet offers better separation power.
Also, industries that require minimal downtime benefit more from self-cleaning suspended magnets due to their automation. Always consider long-term efficiency, energy use, and maintenance requirements before finalizing your choice.
Consulting an experienced magnetic system provider ensures you select the right magnet that enhances performance, protects your equipment, and improves product quality.
Applications of Suspended Magnets
The Applications of Suspended Magnets cover a wide range of industries where metal contamination must be eliminated to protect machinery and maintain product quality. These magnets play a crucial role in removing ferrous metals from conveyor systems, ensuring smooth operations and reducing costly equipment damage. Whether it’s mining, recycling, cement, or food processing, suspended magnets help improve production efficiency and material purity.
Use of Suspended Magnets in Mining and Quarrying
One of the most important Applications of Suspended Magnets is in the mining and quarrying industry. Here, suspended magnets are installed above conveyor belts to remove iron pieces from ores, stones, and minerals. This prevents damage to crushers, grinders, and other heavy machinery.
They are especially useful in separating tramp iron from raw materials before further processing. By doing so, they reduce downtime, enhance safety, and ensure the production of cleaner and higher-quality minerals. Mining operations often integrate these magnets with different Types of Conveyor Belt Systems to maintain a continuous and efficient separation process.
Role of Suspended Magnets in Recycling Industry
In recycling facilities, the Applications of Suspended Magnets help in separating ferrous metals from mixed waste materials. They are mounted over conveyor belts to automatically pull out iron and steel fragments from plastics, paper, and non-ferrous materials.
This process not only helps recover valuable metal for reuse but also ensures that the remaining materials are pure and ready for further recycling. Suspended magnets are essential in recycling plants for improving the efficiency of sorting systems and maintaining the quality of recovered materials.
Importance in Cement, Coal, and Aggregate Plants
The Applications of Suspended Magnets are also vital in industries like cement, coal, and aggregates. These magnets are placed above conveyor lines to catch metallic impurities from materials such as limestone, coal, or sand.
Removing ferrous contaminants early in the process helps prevent wear and tear on crushers, grinders, and conveyors. This not only extends the lifespan of machinery but also ensures a consistent and high-quality final product. For plants handling large volumes of raw materials, suspended magnets are an essential investment in efficiency and safety.
Use in Food Processing and Chemical Industries
In the food processing and chemical industries, the Applications of Suspended Magnets focus on ensuring purity and compliance with quality standards. These magnets remove fine iron particles and metallic dust from powders, grains, sugar, flour, and other raw ingredients before packaging.
Their use prevents contamination, safeguards consumers, and helps manufacturers maintain hygiene standards required by food safety authorities. Similarly, in chemical production, suspended magnets help protect sensitive equipment and maintain the purity of chemical compounds.
Advantages of Using Suspended Magnets
The Advantages of Suspended Magnets make them a key part of many industrial applications. These powerful devices not only remove unwanted metal pieces but also protect machines, maintain product purity, and improve overall plant efficiency. Whether in mining, food processing, or recycling industries, suspended magnets deliver long-term benefits that enhance productivity and safety.
Protection Against Machine Damage
One of the biggest Advantages of Suspended Magnets is their ability to prevent costly damage to machinery. By capturing ferrous contaminants like nails, bolts, and iron fragments before they enter crushers or grinders, these magnets reduce wear and tear on equipment.
This protection minimizes breakdowns, prevents downtime, and extends the life of expensive industrial machines. In high-load environments such as cement or aggregate plants, suspended magnets act as a first line of defense against mechanical failure, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted operation.
Improved Product Purity and Quality Control
Another major benefit among the Advantages of Suspended Magnets is improved product quality. These magnets ensure that metal impurities are completely removed from the product stream, maintaining high levels of purity in raw materials.
Industries like food processing, recycling, and mining rely on suspended magnets to meet strict quality control standards. By removing ferrous contamination, they help deliver cleaner, safer, and higher-quality final products — which boosts customer satisfaction and brand trust.
Cost Savings and Easy Maintenance
Cost efficiency is one of the most practical Advantages of Suspended Magnets. Since they prevent equipment damage and reduce the need for repairs, they save significant maintenance expenses over time.
Permanent suspended magnets require minimal upkeep, and even electromagnetic types are designed for durability and long service life. Installation is simple, and routine cleaning ensures long-term efficiency. When combined with reliable components from an experienced SMSR Gearbox manufacturer, they further contribute to smooth material handling and reduced operational costs.
Energy Efficiency and Long-Term Reliability
Among the top Advantages of Suspended Magnets is their energy efficiency. Permanent magnets do not require power, making them an eco-friendly choice for continuous operations. Even electromagnetic magnets are designed for optimized energy use, allowing operators to adjust power levels based on process requirements.
Their sturdy construction, resistance to harsh environments, and consistent performance make them a long-term solution for industrial metal separation. Over years of operation, suspended magnets continue to deliver reliable results, ensuring steady production and minimal downtime.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding What Is a Suspended Magnet helps us recognize its importance across multiple industries. These powerful magnetic separators play a crucial role in removing unwanted ferrous materials from conveyor systems, ensuring equipment safety, product purity, and efficient production.
From mining and recycling to food processing and cement manufacturing, suspended magnets have become essential for maintaining quality standards and reducing costly downtime. Their wide range of benefits — including energy efficiency, durability, and low maintenance — make them a smart investment for any industrial operation.
Whether permanent or electromagnetic, each type serves a specific purpose depending on material flow and contamination levels. By choosing the right design and working with reliable manufacturers, businesses can greatly enhance productivity and safety.
Ultimately, the use of suspended magnets reflects a proactive approach to quality control and equipment protection. For industries aiming to improve performance and reliability, these magnets are a simple yet powerful solution that ensures long-term efficiency and cleaner production.
FAQS
What Is a Suspended Magnet used for?
A suspended magnet is used to remove unwanted ferrous metals from conveyor belts or material flow. It protects machines from damage and improves product quality by ensuring only clean materials pass through.
How does a Suspended Magnet increase machine life?
A suspended magnet removes metal contaminants before they reach crushers or grinders, reducing wear and tear. This extends machine life and lowers maintenance costs for industrial operations.
Can a Suspended Magnet work with any type of conveyor belt?
Yes, most suspended magnets can be installed above flat or trough conveyor belts. However, the right size and type depend on the Types of Conveyor Belt Systems and the material being handled.
What materials can a Suspended Magnet separate?
Suspended magnets attract and remove ferrous materials like nails, bolts, iron pieces, and steel fragments. They do not work on non-ferrous materials such as aluminum, copper, or plastic.
How often should a Suspended Magnet be cleaned?
Cleaning frequency depends on the level of contamination. Manual cleaning may be needed daily in heavy-duty plants, while self-cleaning suspended magnets require minimal maintenance.
What are the installation requirements for a Suspended Magnet?
A suspended magnet should be positioned above a conveyor at an ideal height to capture metal contaminants efficiently. Proper alignment ensures maximum separation performance.
What Is a Suspended Magnet’s role in the food industry?
Suspended magnets are made from strong magnetic materials like ferrite or rare-earth magnets, enclosed in a durable stainless-steel casing for protection in harsh industrial environments.
Are Suspended Magnets energy-efficient?
Yes, especially permanent suspended magnets, which do not require power to operate. Electromagnetic versions use controlled energy efficiently, offering powerful performance with minimal energy use.
How to choose the right Suspended Magnet for your plant?
To select the right model, consider your material type, belt width, speed, and contamination level. Consulting an expert or trusted Suspension magnet manufacturer ensures the perfect match for your industry needs