What Is an Electric Motor? A Complete Guide
Electric motors are an essential part of everyday life, even though they often work silently in the background. From home appliances like fans and washing machines to industrial machines, pumps, conveyors, and electric vehicles, electric motors make modern living and industrial operations possible. As the demand for energy-efficient and reliable machines continues to grow, many people search online to understand what an electric motor is, how it works, and where it is used.
This complete guide to electric motors is written to provide a clear and easy-to-understand explanation for beginners as well as professionals. Instead of using complex technical terms, the guide explains the fundamentals in a simple and practical manner. You will learn about the basic working principle of an electric motor, its main components, different types of electric motors, and their real-world applications across industries.
The content is structured to answer common questions people search for on Google, making it useful for students, engineers, technicians, and business owners. It focuses on real-life usage and practical understanding rather than theory alone, including insights into industrial use cases such as Conveyor Belt Application. By the end of this guide, you will have a strong foundation in electric motors, helping you understand how they function, why they are important, and how to choose the right motor for different applications.
What Is an Electric Motor?
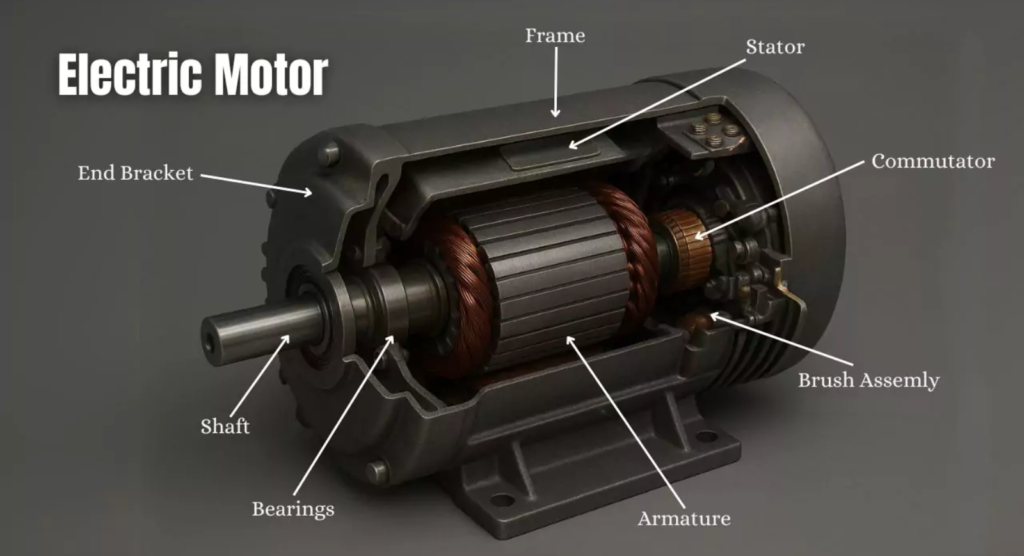
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to create motion. In simple terms, it takes electricity as input and produces rotating movement that can be used to run machines, tools, and equipment. When people search What Is an Electric Motor?, they usually want a clear and easy explanation of how this device works and why it is so important in daily life and industry.
An electric motor works using the interaction between an electric current and a magnetic field. When current flows through the motor, it creates magnetic force, which causes the motor shaft to rotate. This rotation is then used to perform useful work such as turning a fan, pumping water, moving a conveyor belt, or powering industrial machines.
Today, electric motors are everywhere. You can find them in home appliances, factories, vehicles, and automation systems. They are preferred because they are efficient, reliable, and easy to control. Understanding What Is an Electric Motor? helps users make better decisions when selecting motors for different applications, whether for household use or large-scale industrial operations.
In short, an electric motor is the backbone of modern technology, enabling smooth operation, energy efficiency, and consistent performance across countless applications.
How Does an Electric Motor Work?
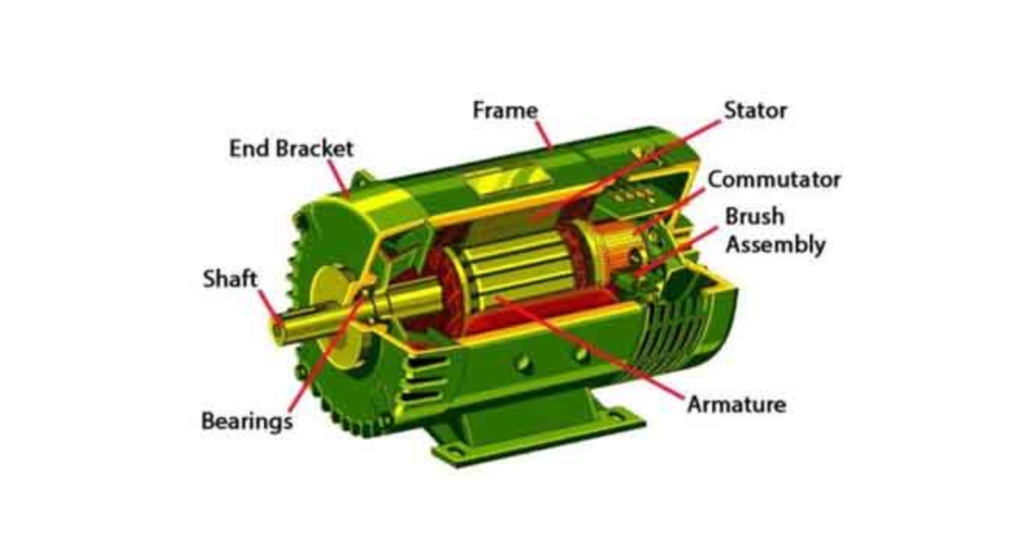
An electric motor works by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of electric current and magnetic fields. When electricity flows through the motor’s coils, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with another magnetic field inside the motor, producing a force that causes the motor’s shaft to rotate. This rotating motion is what allows machines and devices to perform useful work and is widely used in industrial systems supported by components supplied by a plummer block manufacturer.
To understand How Does an Electric Motor Work?, it is helpful to look at the process in simple terms. Electricity enters the motor and passes through the windings placed inside a magnetic field. As soon as current flows, a force is generated that pushes the rotor to move. The design of the motor ensures that this movement continues in a circular motion, creating steady rotation instead of stopping after one turn.
In basic operation, an electric motor works in the following way:
- Electrical power is supplied to the motor windings
- A magnetic field is produced around the windings
- The magnetic interaction creates force on the rotor
- The rotor starts rotating and delivers mechanical output
This continuous rotation can be used to run fans, pumps, conveyors, compressors, and many other machines. Understanding How Does an Electric Motor Work? helps users see why electric motors are efficient, reliable, and widely used in both household and industrial applications.
Types of Electric Motors
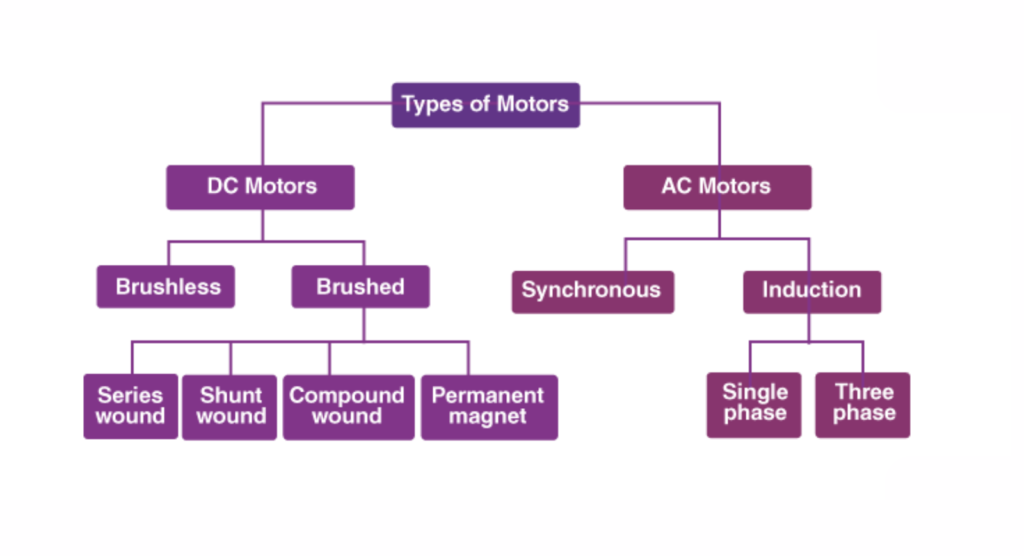
There are different types of electric motors, and each type is designed to perform a specific task based on power supply, speed requirement, load condition, and application. Understanding the types of electric motors helps users choose the right motor for better efficiency, safety, and long-term performance. These motors are mainly classified into AC motors, DC motors, and special-purpose motors.
1. AC Electric Motors
AC electric motors operate on alternating current and are the most commonly used motors in industries and commercial systems. They are popular because of their simple design, low maintenance, and long operating life.
- Induction Motor
The induction motor is the most widely used electric motor in the world. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where current is induced in the rotor when the stator produces a rotating magnetic field.
The rotor starts rotating slightly slower than the magnetic field speed, which creates motion. Induction motors are known for their strong construction, high reliability, and ability to run continuously for long hours. They are commonly used in pumps, fans, compressors, conveyor belts, and industrial machinery.
- Synchronous Motor
A synchronous motor rotates at a constant speed that is exactly synchronized with the supply frequency. Unlike induction motors, there is no slip between the rotor and the magnetic field. These motors are used where constant speed is required, regardless of load changes.
Synchronous motors are often found in power plants, large industrial compressors, and heavy-duty material handling setups that operate across different types of conveyor belt systems, where stable speed and precise control are essential for smooth and efficient operation.
- Single Phase Motor
Single phase motors are designed to work on single phase power supply, which is commonly available in homes and small commercial places. These motors are simple in design and suitable for low-power applications.
Because single phase supply cannot create a rotating magnetic field on its own, additional components like capacitors are used to start the motor. Single phase motors are used in ceiling fans, washing machines, water pumps, and small air conditioning units.
- Three Phase Motor
Three phase motors operate on three phase power supply and are mainly used in industrial environments. They provide higher efficiency, better torque, smoother operation, and lower power loss compared to single phase motors.
These motors start automatically without additional starting devices and are ideal for heavy-duty applications. Common uses include elevators, cranes, rolling mills, large pumps, and factory equipment.
2. DC Electric Motors
DC electric motors run on direct current and are mainly used where precise speed control and high starting torque are required.
- Brushed DC Motor
Brushed DC motors use brushes and a commutator to supply current to the rotating part of the motor. They are easy to control and inexpensive, making them suitable for simple applications. However, brushes wear out over time, which increases maintenance. These motors are commonly used in toys, portable tools, automotive systems, and small machines.
-Brushless DC Motor (BLDC)
Brushless DC motors do not use brushes, which reduces friction, heat, and maintenance. Instead, electronic controllers manage the motor operation.
BLDC motors are highly efficient, quiet, and have a long service life. They are widely used in electric vehicles, drones, computer cooling fans, air conditioners, and modern household appliances.
3.Special Purpose Electric Motors
Special purpose motors are designed for applications that require precise control, accuracy, or specific motion.
-Servo Motor
Servo motors are used in systems where accurate control of position, speed, and torque is required. They use a feedback mechanism to compare actual position with the desired position and correct errors instantly. Servo motors are commonly used in robotics, CNC machines, automated manufacturing lines, and industrial control systems.
-Stepper Motor
Stepper motors move in fixed steps rather than continuous rotation. This allows very precise positioning without the need for feedback systems. Stepper motors are easy to control and are widely used in 3D printers, medical equipment, cameras, and digital measuring instruments.
-Linear Motor
A linear motor produces straight-line motion instead of rotational motion. It works on the same electromagnetic principle as rotary motors but eliminates the need for mechanical conversion systems. Linear motors are used in high-speed trains, sliding doors, material handling systems, and precision industrial equipment.
Applications of Electric Motors Across Industries
The applications of electric motors vary across multiple industries, where they are used to power machines, automate processes, and improve productivity. Each industry depends on electric motors for reliable motion, energy efficiency, and continuous operation.
Below are the major industries where electric motors play a critical role, explained in a clear and practical way, with support from essential components supplied by a UCP Pillow Block manufacturer that ensure smooth shaft alignment and reliable machine performance.
1. Manufacturing Industry
In the manufacturing industry, electric motors are used to run production lines, machine tools, and automated systems. They power equipment such as lathes, milling machines, presses, and assembly conveyors.
The applications of electric motors in manufacturing help maintain consistent speed, improve product quality, and reduce manual effort.
2. Mining Industry
The mining industry relies heavily on electric motors for heavy-duty operations. Motors are used in crushers, drilling machines, conveyor belts, and ventilation systems. These applications of electric motors support continuous operation in harsh environments while ensuring safety and efficiency.
3. Cement Industry
In the cement industry, electric motors are used to operate crushers, kilns, ball mills, and material handling systems. Motors help manage high-load operations and maintain smooth production flow, making them essential for large-scale cement plants.
4. Power Generation Industry
Electric motors are widely used in power plants for running pumps, cooling fans, compressors, and auxiliary systems. The applications of electric motors in this industry support reliable power generation and system stability.
5. Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry uses electric motors in drilling rigs, pumping systems, compressors, and refineries. Motors provide precise control and continuous performance in demanding and hazardous environments.
6. Water and Wastewater Treatment Industry
In water treatment plants, electric motors are used to run pumps, aerators, mixers, and filtration systems. These applications of electric motors ensure efficient water distribution, purification, and wastewater management.
7. Food and Beverage Industry
The food and beverage industry depends on electric motors for mixers, grinders, packaging machines, and conveyor systems. Motors help maintain hygiene standards, consistent processing, and efficient packaging operations.
8. Automotive and Transportation Industry
Electric motors are essential in electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, railways, and automated transport systems. These applications of electric motors support energy-efficient movement and reduced emissions.
9. HVAC and Building Services Industry
In HVAC systems, electric motors are used in fans, blowers, compressors, and air handling units. The applications of electric motors help control temperature, airflow, and indoor comfort in residential and commercial buildings.
10. Agriculture Industry
In agriculture, electric motors are used in irrigation pumps, grain processing machines, dairy equipment, and farm automation systems. These motors improve productivity and reduce manual labor.
Conclusion
Electric motors are the foundation of modern technology, quietly powering countless devices and machines that support daily life and industrial progress. From simple household appliances to complex industrial systems, understanding what an electric motor is helps create a clear picture of how electrical energy is transformed into useful mechanical work. This complete guide has covered the core concepts of electric motors, including how they work, their main types, efficiency levels, and wide-ranging applications across industries.
Knowing the basics of electric motors is no longer limited to engineers or technicians. Business owners, students, and decision-makers also benefit from understanding how electric motors affect energy consumption, performance, and long-term operating costs. Choosing the right motor can improve efficiency, reduce breakdowns, and support sustainable operations in both small and large-scale applications.
As technology continues to evolve, electric motors are becoming more efficient, smarter, and better suited for automation and clean energy systems. Innovations such as high-efficiency motors and advanced control systems are shaping the future of manufacturing, transportation, and renewable energy, often working alongside solutions provided by an SMSR Gearbox manufacturer for effective power transmission. By understanding the fundamentals explained in this guide, readers are better prepared to make informed choices, optimize performance, and adapt to future developments. In short, electric motors will remain a vital force behind innovation, productivity, and technological growth for years to come.
FAQS
What is an electric motor in simple words?
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It uses electricity and magnetism to produce motion. This motion is used to run devices like fans, pumps, machines, and vehicles, making electric motors essential in homes, industries, and modern technology.
How does an electric motor work step by step?
An electric motor works by allowing electric current to flow through coils placed in a magnetic field. This interaction creates force that causes the rotor to rotate. Continuous supply of electricity maintains rotation, producing mechanical energy that powers machines, tools, and equipment.
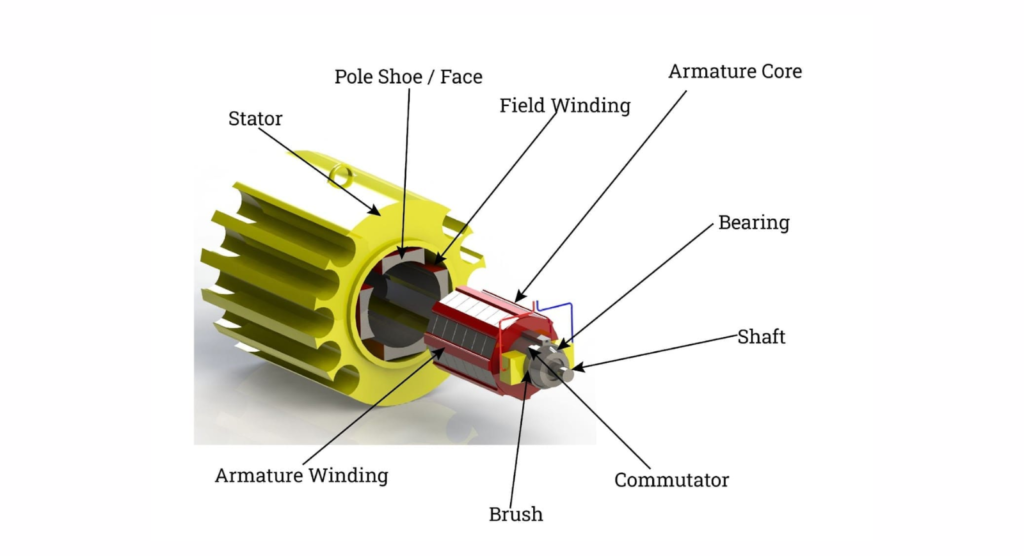
What are the main parts of an electric motor?
The main parts of an electric motor include the stator, rotor, windings, shaft, bearings, and cooling system. The stator creates the magnetic field, while the rotor rotates to produce motion. Bearings reduce friction, and cooling systems prevent overheating during operation.
What are the different types of electric motors?
Electric motors are mainly classified into AC motors, DC motors, single phase motors, three phase motors, and special motors like servo and stepper motors. Each type is designed for specific power supply conditions, speed control needs, and applications in household, commercial, and industrial use.
Where are electric motors used in daily life?
Electric motors are widely used in daily life through appliances such as fans, washing machines, refrigerators, air conditioners, mixers, and water pumps. They are also used in elevators, escalators, electric vehicles, and automated systems that make everyday tasks easier and more efficient.
What is the difference between AC motor and DC motor?
An AC motor operates on alternating current and is commonly used in industrial and commercial applications due to its durability and low maintenance. A DC motor runs on direct current and is preferred where precise speed control, high starting torque, and flexible operation are required.
What is electric motor efficiency?
Electric motor efficiency refers to how well a motor converts electrical input power into useful mechanical output power. Higher efficiency means less energy loss as heat, lower electricity consumption, reduced operating cost, and better overall performance, especially in continuous industrial applications.
Why do electric motors overheat?
Electric motors overheat due to overload, poor ventilation, voltage imbalance, frequent starting, bearing failure, or lack of maintenance. Overheating reduces motor efficiency and lifespan. Proper motor selection, regular servicing, and adequate cooling help prevent overheating problems.
What are the main applications of conveyor belts?
Conveyor belts are mainly used for transporting materials and products in industries such as mining, cement, manufacturing, food processing, agriculture, logistics, and warehousing. They support continuous material movement, reduce manual handling, and improve operational efficiency.
Which industries use conveyor belt systems the most?
Industries that use conveyor belt systems the most include mining, cement plants, manufacturing units, food processing facilities, agriculture, power plants, and logistics centers. These industries rely on conveyor belts for bulk material handling and continuous production flow.
Why are conveyor belts important in industrial applications?
Conveyor belts are important because they improve productivity, reduce labor costs, enhance safety, and ensure consistent material flow. They help industries automate processes and maintain smooth operations even in high-volume environments.
How do conveyor belts improve productivity in industries?
Conveyor belts improve productivity by enabling continuous and controlled movement of materials. They reduce delays, minimize manual handling, and help maintain a steady workflow across different production stages.
What types of conveyor belts are used for different applications?
Different applications use different conveyor belts, such as flat belts, troughed belts, cleated belts, heat-resistant belts, and food-grade belts. The selection depends on material type, load capacity, temperature, and operating conditions.
Where are conveyor belts used in mining and cement industries?
In mining and cement industries, conveyor belts are used for transporting raw materials, clinker, coal, minerals, and finished products. They support long-distance and heavy-load material handling in harsh environments.
How do conveyor belt systems support automation?
Conveyor belt systems support automation by connecting multiple processes into a continuous workflow. This reduces human intervention, improves accuracy, and helps industries scale production efficiently.
How do conveyor belt systems support automation?
Conveyor belt systems support automation by connecting multiple processes into a continuous workflow. This reduces human intervention, improves accuracy, and helps industries scale production efficiently.
How to choose the right conveyor belt for an application?
The right conveyor belt is chosen based on factors such as material type, load weight, operating environment, temperature conditions, and production requirements. Selecting the correct belt ensures durability, safety, and long-term performance

