Top 10 UCP Pillow Block Manufacturers in Rajasthan
Rajasthan is rapidly emerging as a strong industrial hub in India, with growing demand for advanced material handling and magnetic separation equipment. Industries such as mining, cement, recycling, and bulk material processing require reliable solutions to remove unwanted ferrous metals from conveyor systems. This is where suspension magnets play a critical role. Businesses searching for a trusted Suspension Magnet Manufacturer in Rajasthan often look for companies that combine high magnetic strength, durable construction, and consistent performance in demanding industrial environments.
Several manufacturers in the region are known for producing high-quality suspension magnets designed to improve operational efficiency and protect costly machinery from metal contamination. Choosing the right Suspension Magnet Manufacturer in Rajasthan can significantly enhance production safety, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure smooth industrial operations. From permanent suspension magnets to electromagnetic systems, modern manufacturers offer a wide range of magnetic separation solutions tailored for different industries. A reliable SMSR Gearbox manufacturer also plays an important role in supporting conveyor-driven industrial systems.
In this article, we will explore the Top 10 Suspension Magnet Manufacturers in Rajasthan, starting with Nisuka Industries, a trusted name known for its advanced magnetic technology and industrial expertise. This curated list will help businesses, plant managers, and procurement professionals find reliable manufacturers that deliver quality, innovation, and dependable after-sales support across Rajasthan’s growing industrial landscape.
Here are 10 Suspension Magnet Manufacturers in Rajasthan
1. Nisuka Industries - Leading Suspension Magnet Manufacturer in Rajasthan
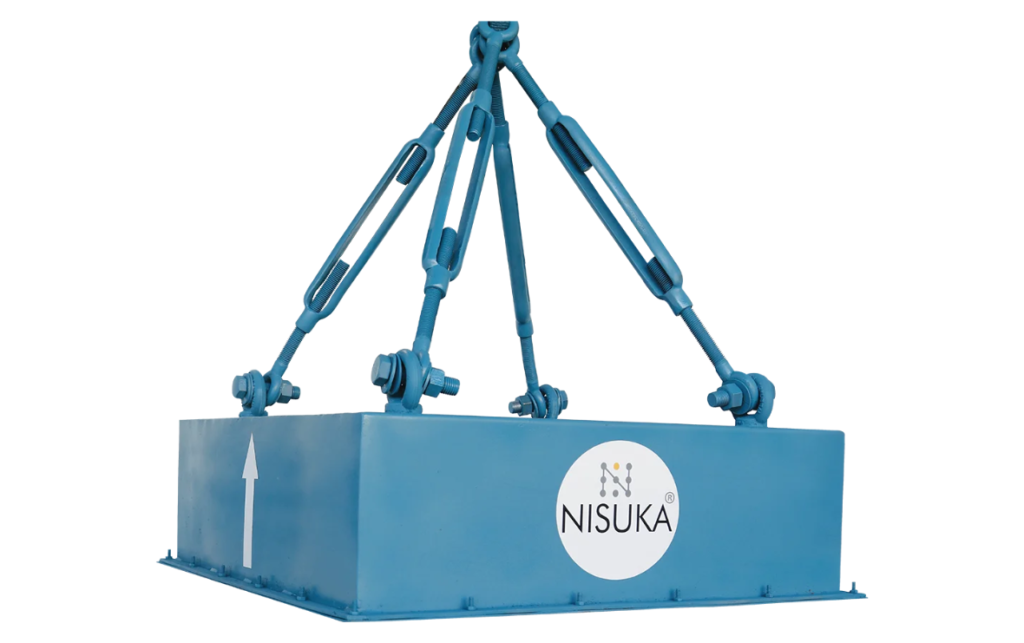

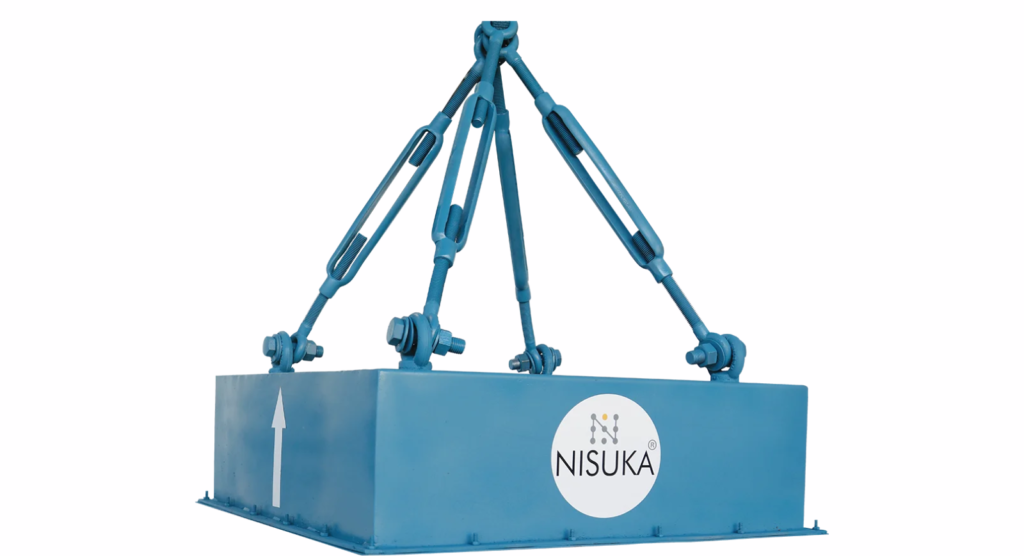
Nisuka Industries is recognized as a trusted Suspension Magnet Manufacturer in Rajasthan, offering advanced magnetic separation solutions for a wide range of industries. With growing industrial activities in sectors such as mining, cement production, recycling, and power generation, the demand for reliable magnetic equipment has increased significantly.
Nisuka Industries has built a strong reputation by manufacturing high-quality suspension magnets that help industries efficiently remove ferrous metal contaminants from conveyor belt systems and bulk materials.
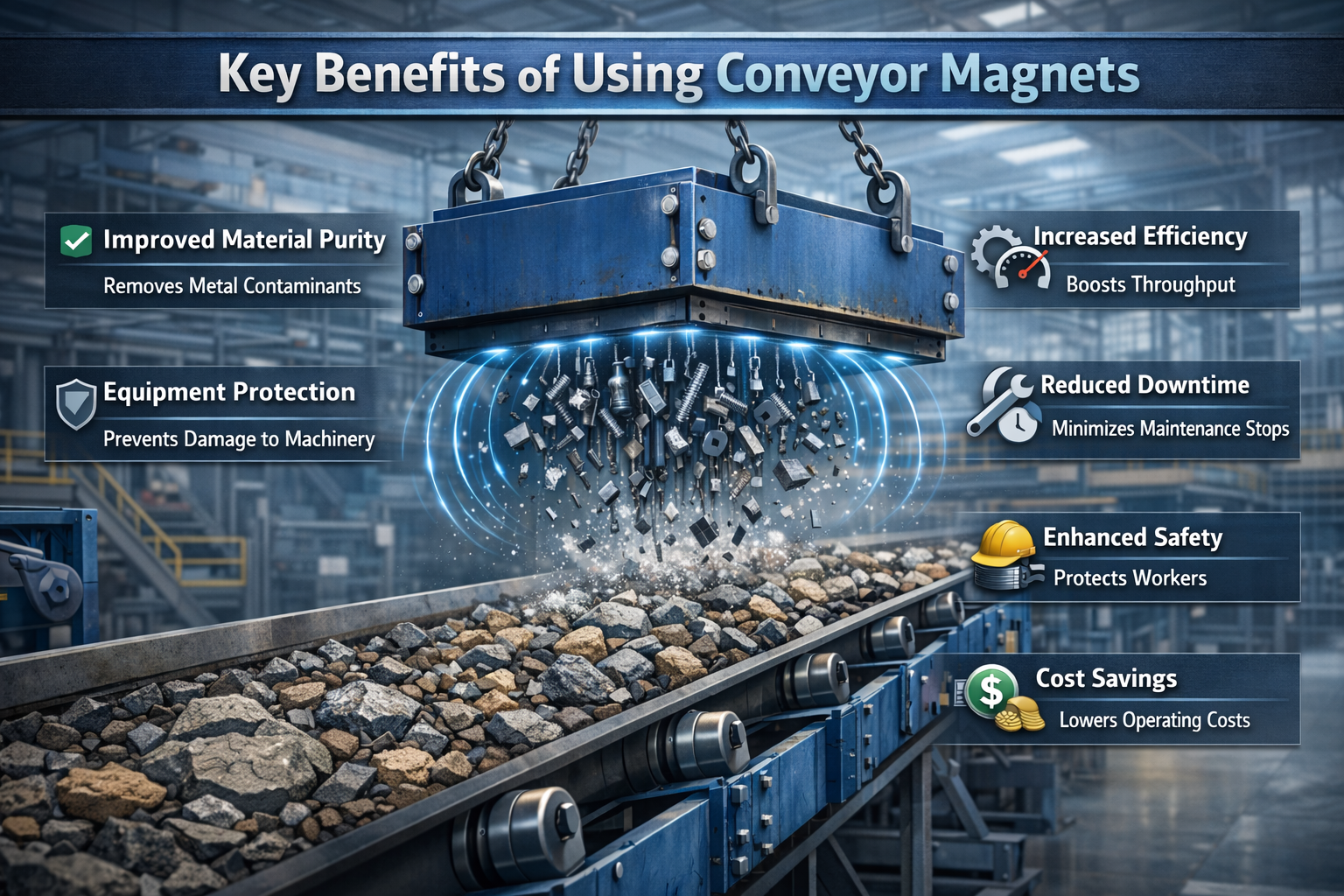
As an experienced Suspension Magnet Manufacturer in Rajasthan, Nisuka Industries focuses on producing durable and high-performance magnetic equipment designed for continuous industrial operations. Suspension magnets are typically installed above conveyor belts to automatically attract and separate unwanted metal pieces from the material flow. This process plays a crucial role in protecting crushers, grinders, and other expensive processing machinery from damage caused by metal contamination. By installing a reliable suspension magnet, industries can reduce downtime, minimize maintenance costs, and maintain smooth production processes.
One of the key strengths of Nisuka Industries as a Suspension Magnet Manufacturer in Rajasthan is its commitment to quality and engineering excellence. The company uses strong magnetic materials and precision manufacturing techniques to ensure that each suspension magnet delivers consistent magnetic strength and long operational life. These magnets are designed to operate efficiently even in harsh industrial environments where heavy materials move continuously through conveyor systems.
Key Features of Nisuka Industries Suspension Magnets
- High magnetic strength for effective removal of ferrous metal
- Strong and durable construction for long-term industrial use
- Easy installation above conveyor belt systems
- Low maintenance and reliable performance
- Suitable for heavy-duty material handling applications
Products Offered by Nisuka Industries
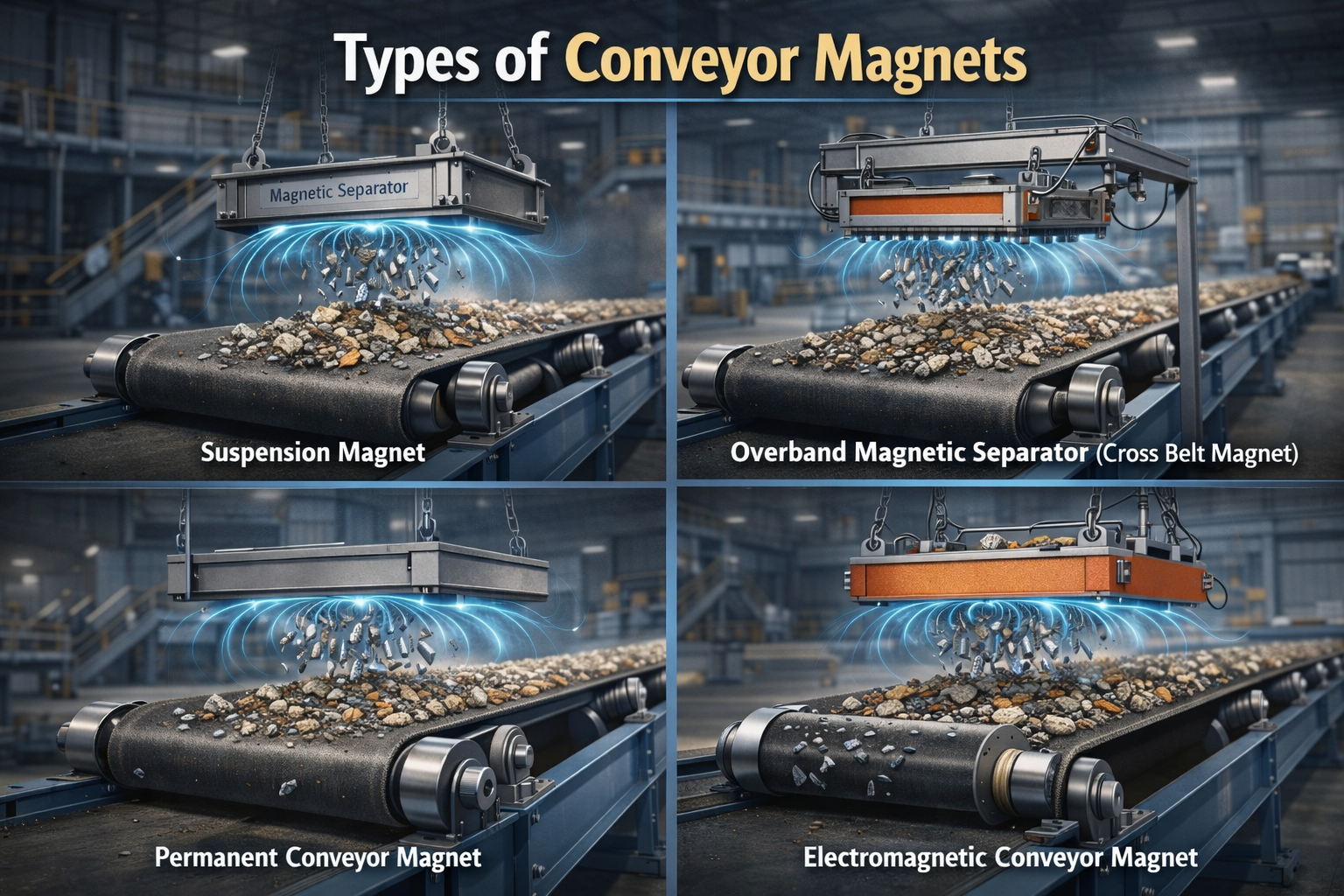
Nisuka Industries offers a wide range of magnetic separation equipment to meet different industrial needs. As a leading Suspension Magnet Manufacturer in Rajasthan, the company manufactures:
- Permanent Suspension Magnets
- Electromagnetic Suspension Magnets
- Overband Magnetic Separators
- Customized Magnetic Separation Systems
Another important factor that makes Nisuka Industries a preferred Suspension Magnet Manufacturer in Rajasthan is its ability to provide customized solutions. Different industries have different conveyor widths, material flow rates, and operational requirements. Nisuka Industries works closely with clients to design suspension magnets that match specific industrial applications, ensuring maximum separation efficiency and performance.
With years of experience, technical expertise, and a strong focus on customer satisfaction, Nisuka Industries continues to support industries across Rajasthan and India. Their commitment to quality, innovation, and reliable magnetic technology has positioned the company as a dependable Suspension Magnet Manufacturer in Rajasthan, helping businesses improve operational safety, productivity, and equipment protection.
2. Shree Vishwakarma Magnets
Shree Vishwakarma Magnets is a well-known company providing magnetic separation equipment for industrial applications. The company manufactures electromagnetic suspension magnets designed for conveyor belt systems used in mining, cement, and recycling industries. Many factories prefer their products because they are durable and efficient in removing ferrous metal contamination from bulk materials.
As a reliable Suspension Magnet supplier in Rajasthan, the company focuses on quality engineering and dependable performance. It also serves clients across India and overseas markets, making it a recognized Suspension Magnet exporter in Rajasthan for industries that require strong and reliable magnetic separation solutions.
3. Regal Magnetics
Regal Magnetics is known for manufacturing and supplying different types of industrial magnets and magnetic separation equipment. The company offers suspended magnets that help industries remove metal impurities from conveyor belts and processing systems. These magnets are widely used in cement plants, recycling facilities, and mineral processing units.
Businesses often choose Regal Magnetics because of its consistent product quality and reliable service. As a trusted Suspension Magnet supplier in Rajasthan, the company supports industrial plants that require efficient metal separation. With growing demand from different industries, Regal Magnetics is also gaining recognition as a Suspension Magnet exporter in Rajasthan serving international markets.
4. Kumar Magnet Industries
Kumar Magnet Industries is one of the established manufacturers of magnetic separation equipment in India. The company produces high-power suspension magnets, magnetic pulleys, and magnetic separators used in industrial material handling systems. These magnets are designed to remove unwanted metal from conveyor systems and protect machinery from damage. Industries such as recycling, cement, and mining rely on their products for efficient operations.
The company has built a strong reputation as a dependable Suspension Magnet supplier in Rajasthan, providing high-quality magnetic equipment. Due to its strong distribution network, Kumar Magnet Industries is also recognized as a growing Suspension Magnet exporter in Rajasthan.
5. Jaykrishna Magnetics Pvt. Ltd.
Jaykrishna Magnetics Pvt. Ltd. is a well-known manufacturer of magnetic separation systems with decades of experience in the industry. The company designs suspension magnets that are widely used in conveyor belt systems for removing ferrous contamination. These products are commonly used in food processing, recycling, mining, and chemical industries. Their focus on research and engineering innovation helps them deliver efficient magnetic equipment.
Many industrial plants rely on them as a trusted Suspension Magnet supplier in Rajasthan because of their consistent quality and technical support. With global clients in different countries, the company is also recognized as a reliable Suspension Magnet exporter in Rajasthan.
6. Electro Flux Equipments Pvt. Ltd.
Electro Flux Equipments Pvt. Ltd. manufactures a wide range of industrial magnetic equipment, including electromagnetic suspension magnets used in heavy industrial environments. These magnets are installed above conveyor belts to automatically remove metal contaminants from bulk materials.
The company serves industries such as coal handling plants, cement manufacturing, steel processing, and mining operations. With strong engineering expertise, Electro Flux provides reliable magnetic solutions for complex industrial applications. It has built a strong reputation as a professional Suspension Magnet supplier in Rajasthan supporting various manufacturing sectors. The company is also expanding its presence globally as a dependable Suspension Magnet exporter in Rajasthan.
7. Star Trace Private Limited
Star Trace Private Limited is a prominent manufacturer of magnetic separation equipment and industrial processing machinery. The company produces suspension magnets that help remove ferrous metals from conveyor belt systems used in mineral processing and recycling industries. These magnets help protect crushers and grinders from metal damage while improving product purity.
Many industries trust Star Trace for its advanced engineering and reliable equipment. As a growing Suspension Magnet supplier in Rajasthan, the company provides magnetic systems that support efficient industrial operations. Due to its strong international presence, Star Trace is also considered a reliable Suspension Magnet exporter in Rajasthan.
8. Erich Magnetics
Erich Magnetics specializes in designing magnetic separation systems used in conveyor-based material handling applications. The company manufactures suspension magnets that are widely used in industries such as cement plants, food processing units, recycling plants, and mining operations. These magnets help remove metal contamination and improve production safety.
The company focuses on delivering high-quality magnetic equipment with reliable performance and long service life. Because of its strong product quality and industrial expertise, Erich Magnetics has become a dependable Suspension Magnet supplier in Rajasthan. The company also supplies magnetic systems internationally, making it a recognized Suspension Magnet exporter in Rajasthan.
9. Permanent Magnet Ltd. (PML)
Permanent Magnet Ltd. is one of the oldest and most respected companies in the magnetic equipment industry. Established decades ago, the company manufactures suspension magnets, magnetic pulleys, and magnetic separators used in industrial processing plants. Their suspension magnets are designed to remove ferrous metals from conveyor belts and protect machinery from damage.
Industries such as mining, cement, recycling, and chemical processing depend on their magnetic solutions. Because of its strong engineering background and reliable product quality, the company is known as a trusted Suspension Magnet supplier in Rajasthan. It is also widely recognized as a global Suspension Magnet exporter in Rajasthan.
10. Pam Equipments
Pam Equipments manufactures industrial magnetic separation equipment designed for heavy-duty applications. The company produces suspension magnets that are commonly installed above conveyor belts to remove metal contaminants from bulk materials. These magnets are widely used in industries such as mining, cement plants, recycling units, and steel processing facilities.
Pam Equipments focuses on delivering durable magnetic solutions that improve operational safety and efficiency. Many industries rely on the company as a dependable Suspension Magnet supplier in Rajasthan for high-quality magnetic equipment. With expanding industrial demand, Pam Equipments is also developing its reputation as a Suspension Magnet exporter in Rajasthan serving international clients.
Conclusion
Rajasthan has become an important industrial region in India, especially for sectors like mining, cement production, recycling, and heavy material handling. These industries require reliable magnetic separation systems to protect machinery and maintain smooth production processes. Choosing the right manufacturer is therefore essential for ensuring long-term efficiency and operational safety. The companies listed in this article represent some of the Top 10 Suspension Magnet Manufacturers in Rajasthan, known for their quality engineering, strong magnetic performance, and dependable industrial solutions.
From experienced manufacturers like Nisuka Industries to other established magnetic equipment providers, these companies offer suspension magnets designed for different conveyor systems and industrial environments. Their products help remove ferrous metal contamination, reduce equipment damage, and improve overall productivity. Businesses looking for a trusted magnetic equipment partner can rely on these manufacturers for durable and high-performance solutions.
When selecting a suspension magnet manufacturer, it is important to consider factors such as product quality, customization capability, industry experience, and after-sales support. Working with an experienced manufacturer ensures better equipment reliability and long-term operational benefits.
Just like industries often search for the Top 10 UCP Pillow Block Manufacturers in Rajasthan for bearing solutions, finding the right suspension magnet manufacturer is equally important for maintaining safe and efficient industrial operations.
FAQS
Who are the top Suspension Magnet manufacturers in Rajasthan?
Some of the top Suspension Magnet manufacturers in Rajasthan include companies that specialize in magnetic separation equipment used in conveyor systems and material handling industries. Manufacturers like Nisuka Industries and other established magnetic equipment companies provide high-quality suspension magnets designed to remove ferrous metal contaminants from bulk materials. These manufacturers focus on strong magnetic performance, durable construction, and reliable operation for industries such as mining, cement plants, recycling facilities, and power plants.
Which industries use suspension magnets in Rajasthan?
Suspension magnets are widely used in industries that handle bulk materials and require metal contamination removal. These industries include mining, cement manufacturing, recycling plants, coal handling systems, power plants, and food processing units. Companies searching for reliable magnetic equipment often choose suppliers from the top Suspension Magnet manufacturers in Rajasthan because they provide durable and efficient metal separation solutions for heavy industrial environments.
How do I choose the best suspension magnet manufacturer in Rajasthan?
Choosing the best manufacturer requires evaluating factors such as magnetic strength, product durability, customization options, manufacturing experience, and after-sales service. A reliable manufacturer provides strong magnetic separation equipment that can operate efficiently in demanding industrial environments. Businesses often compare multiple companies from the top Suspension Magnet manufacturers in Rajasthan to find a supplier that offers high-quality products, technical expertise, and long-term support for industrial operations.